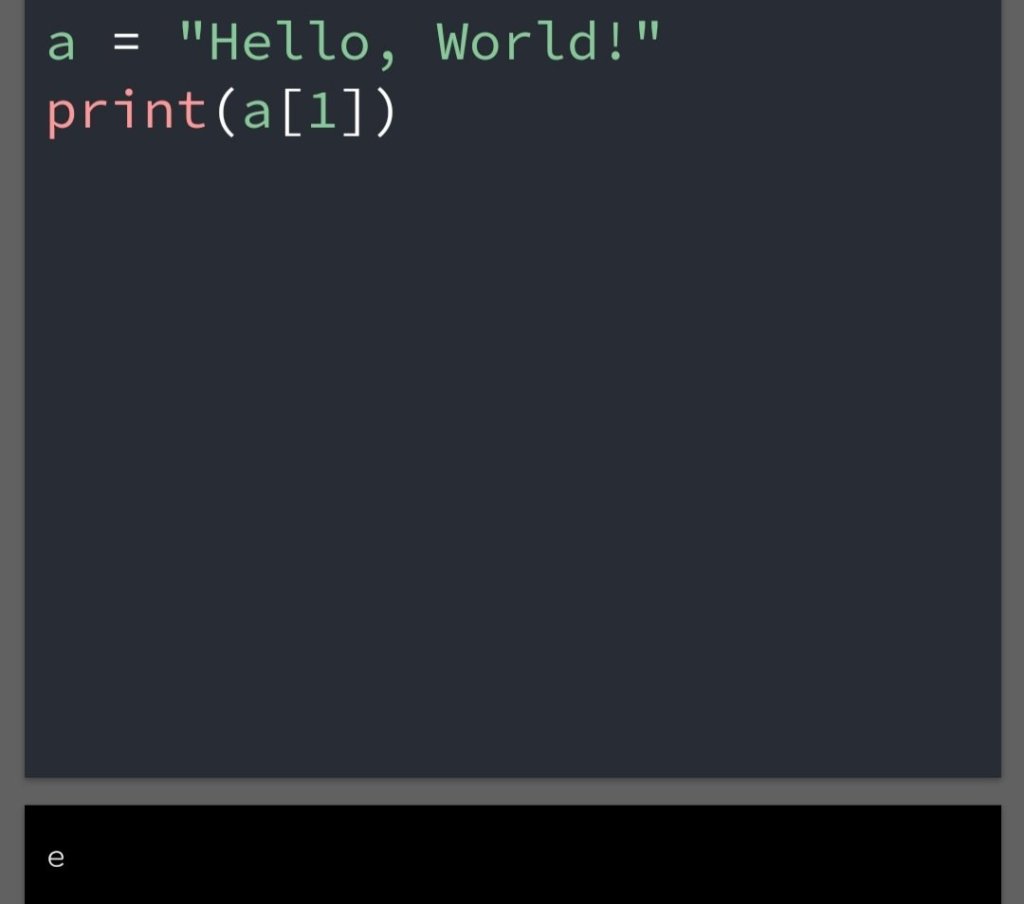
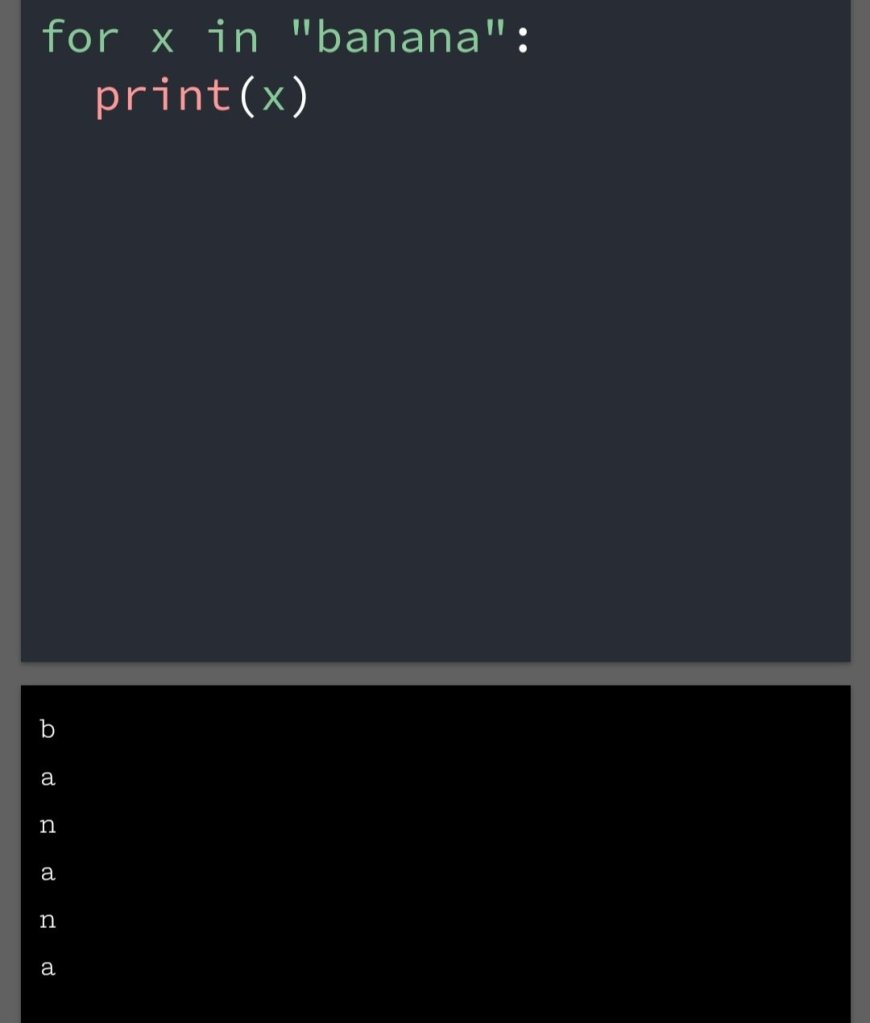
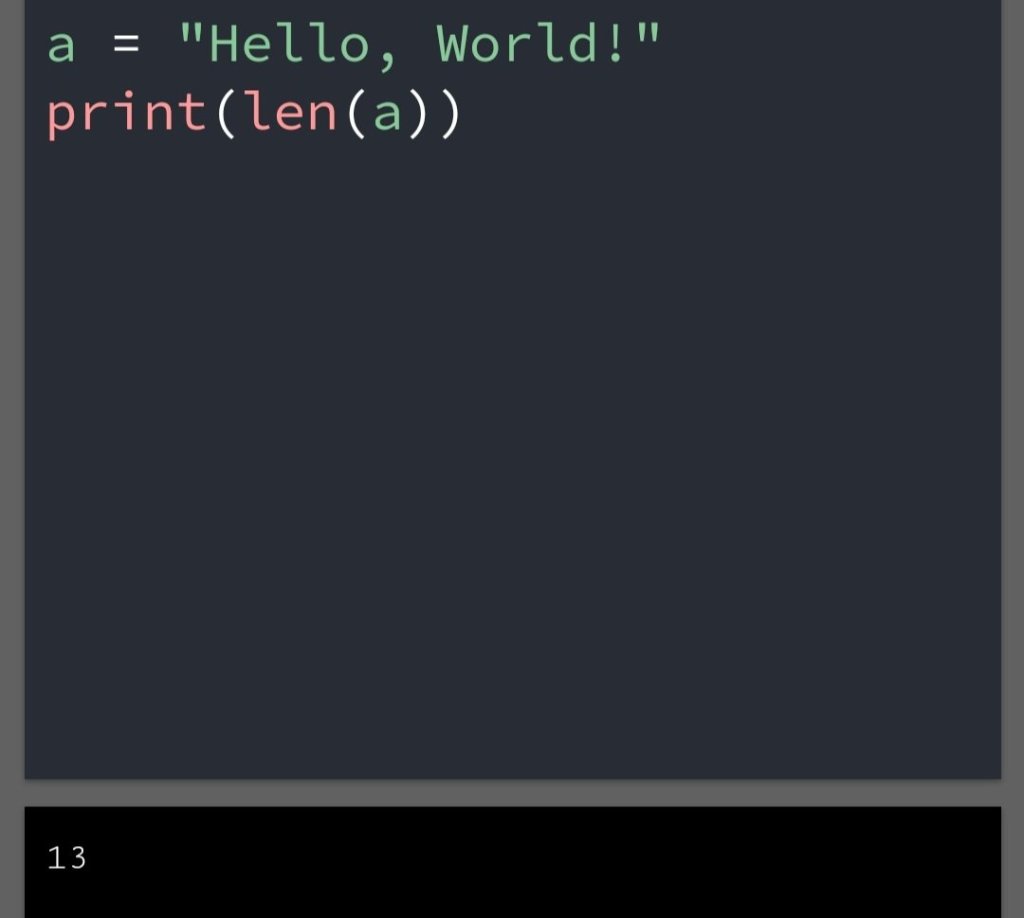
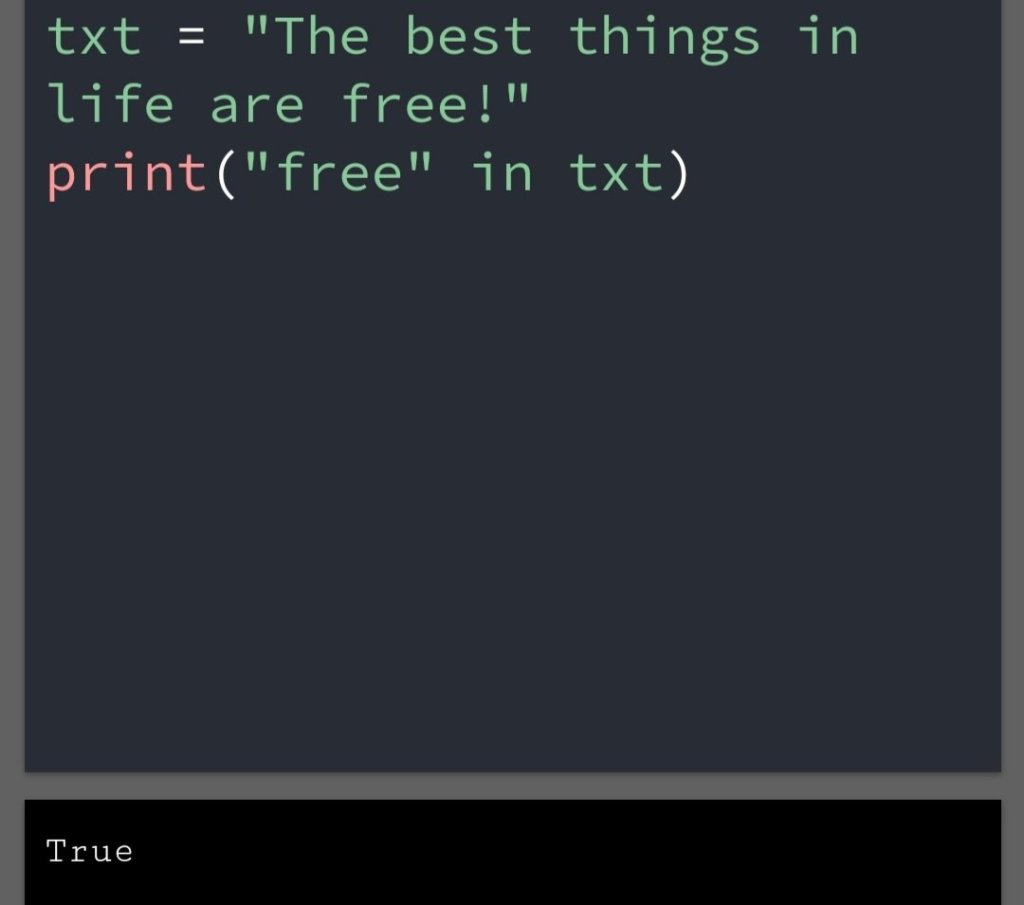
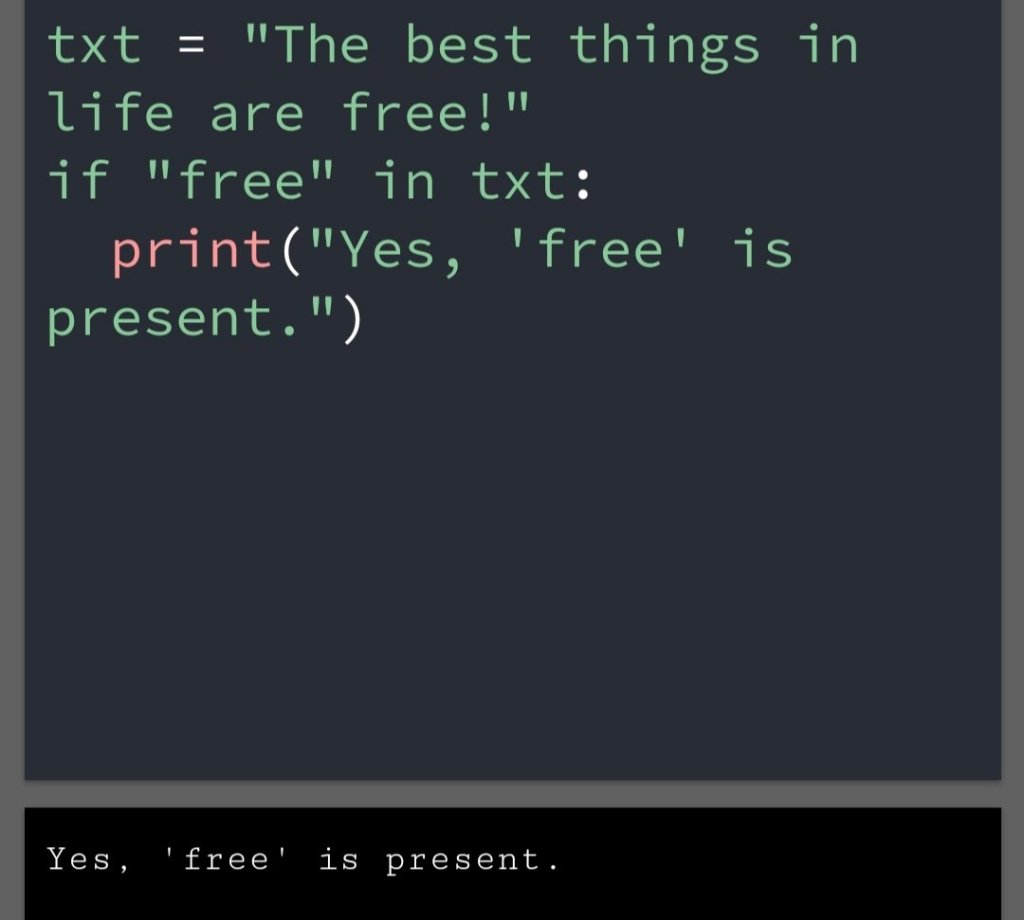
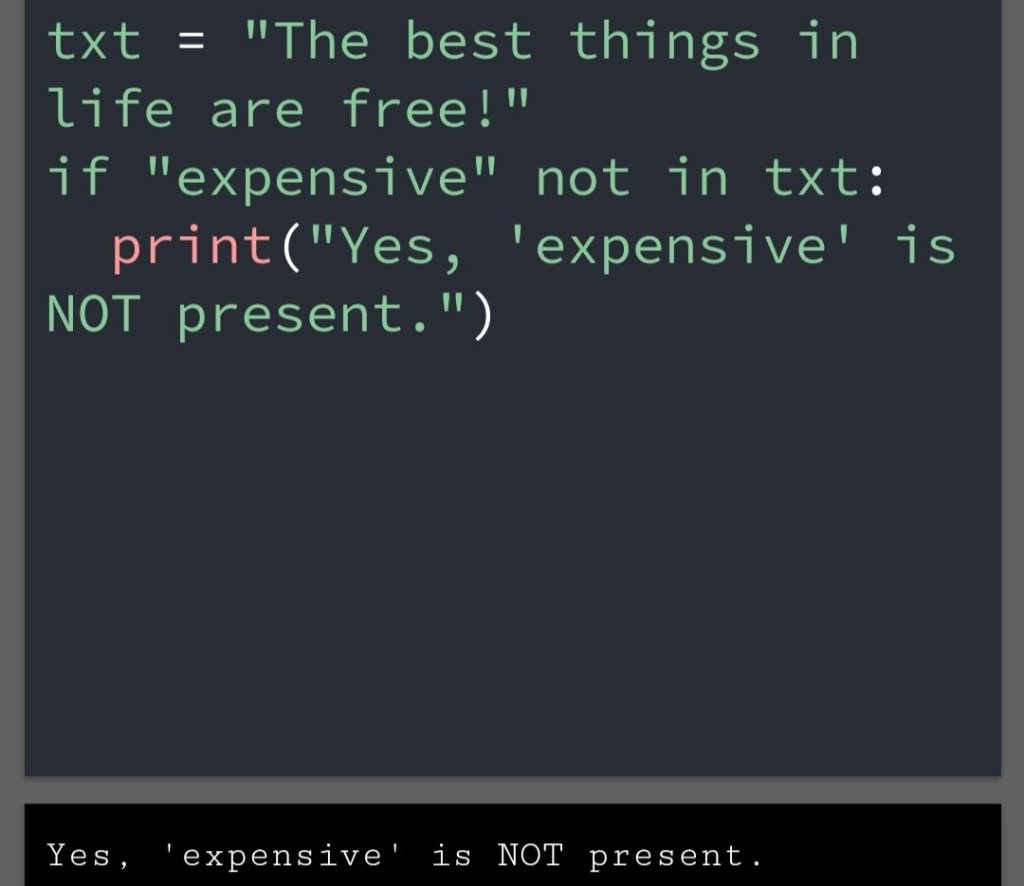
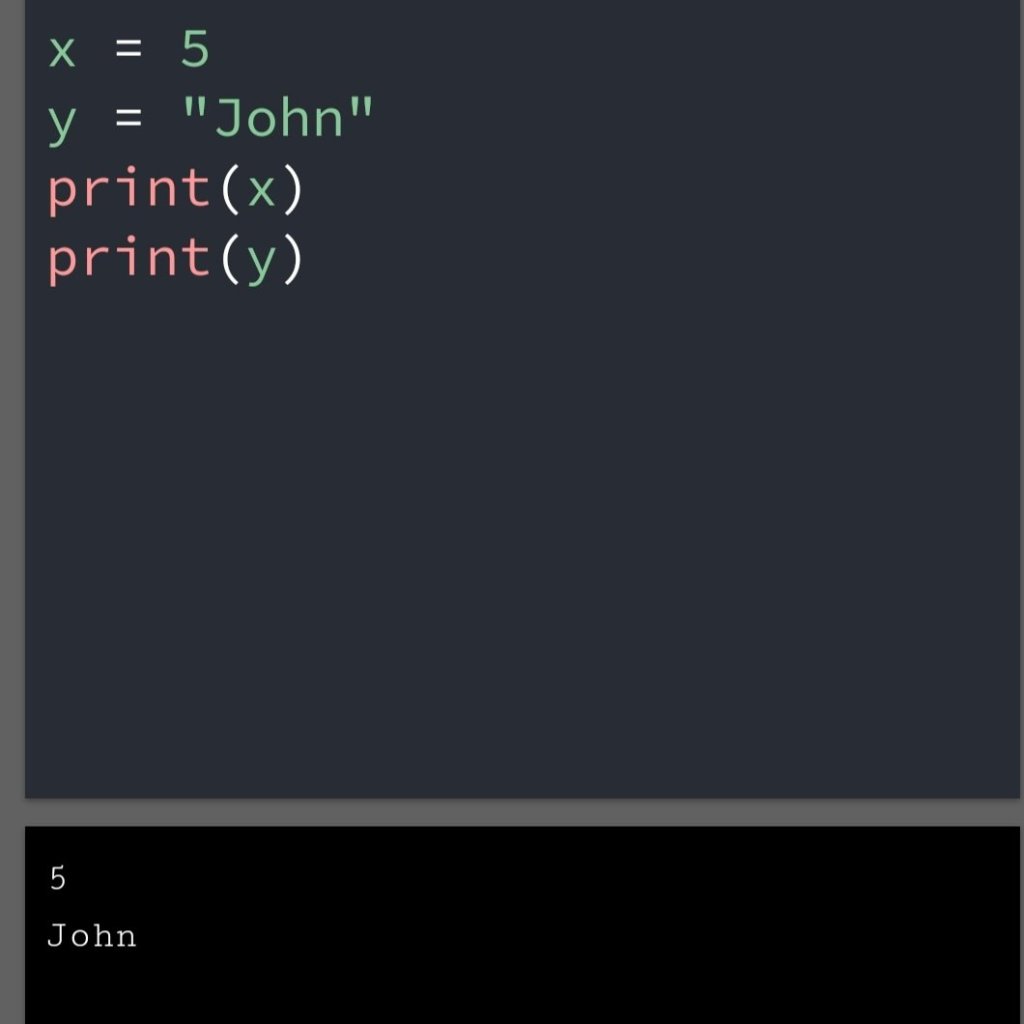
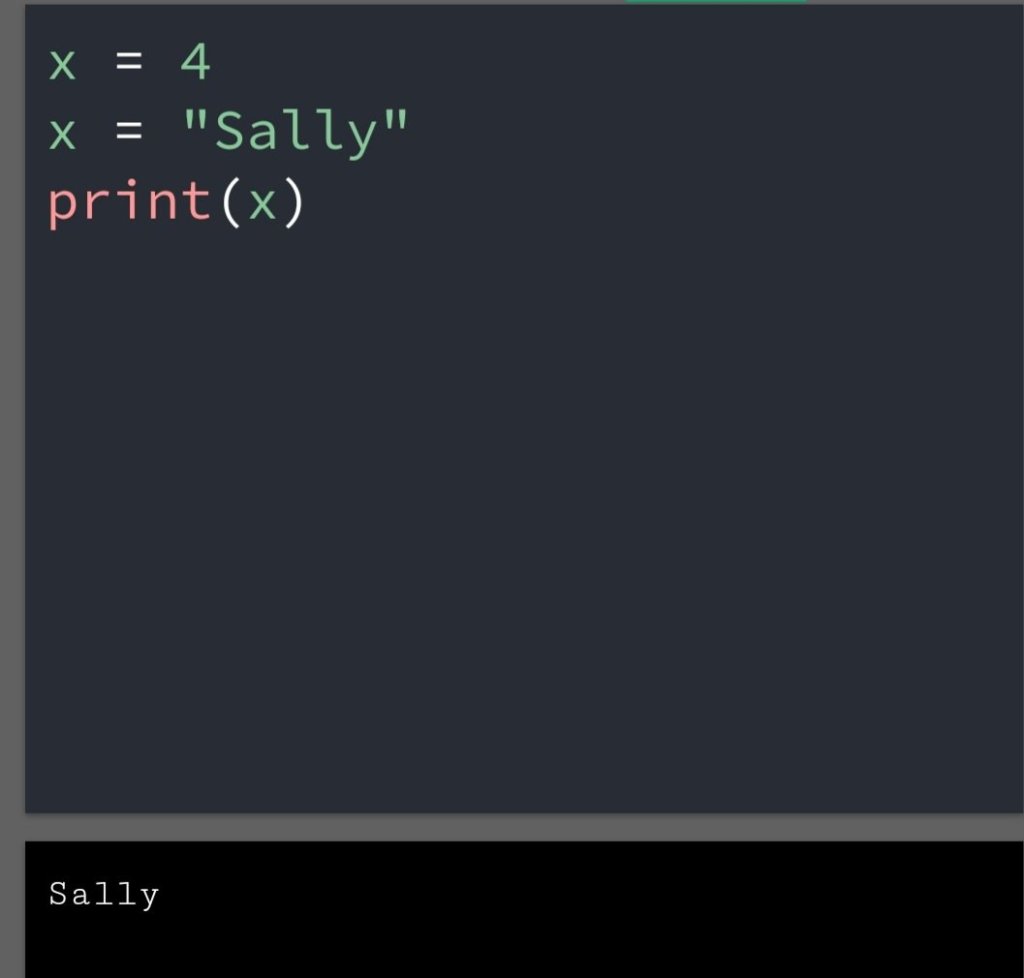
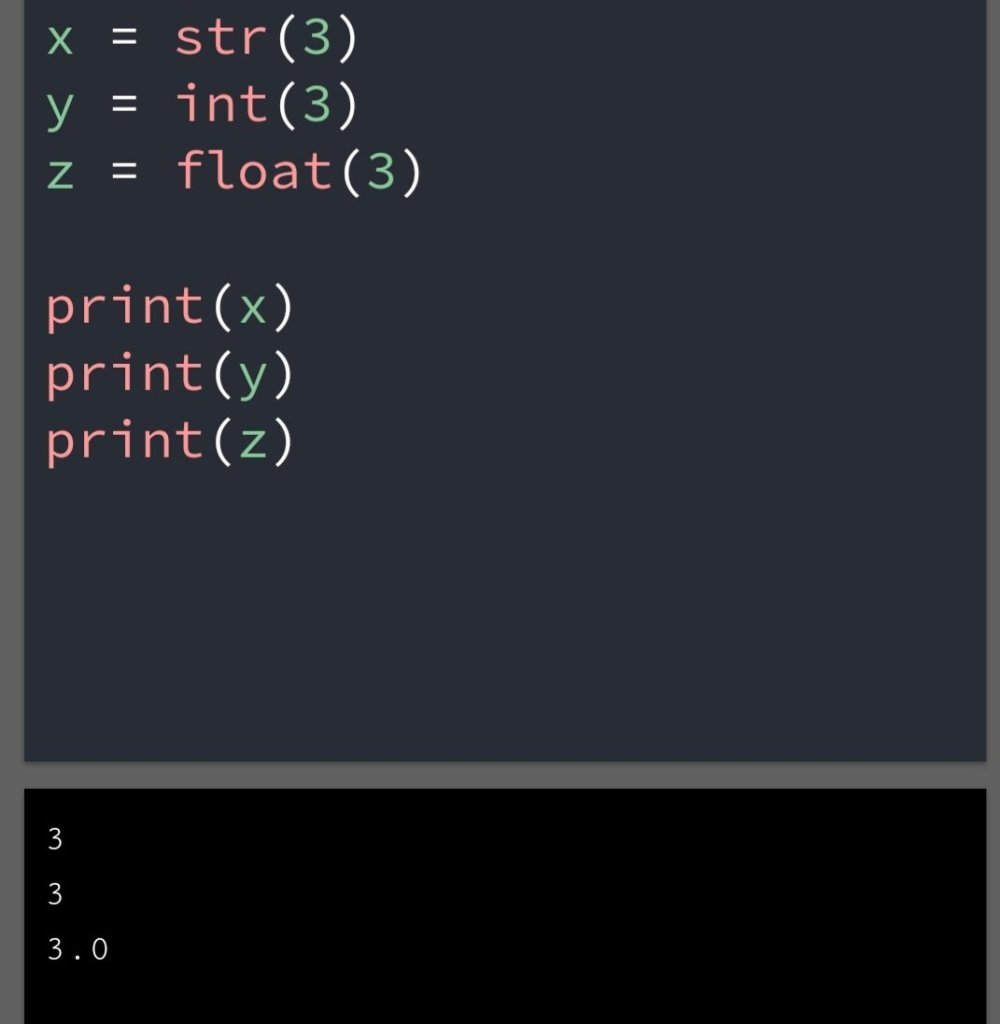
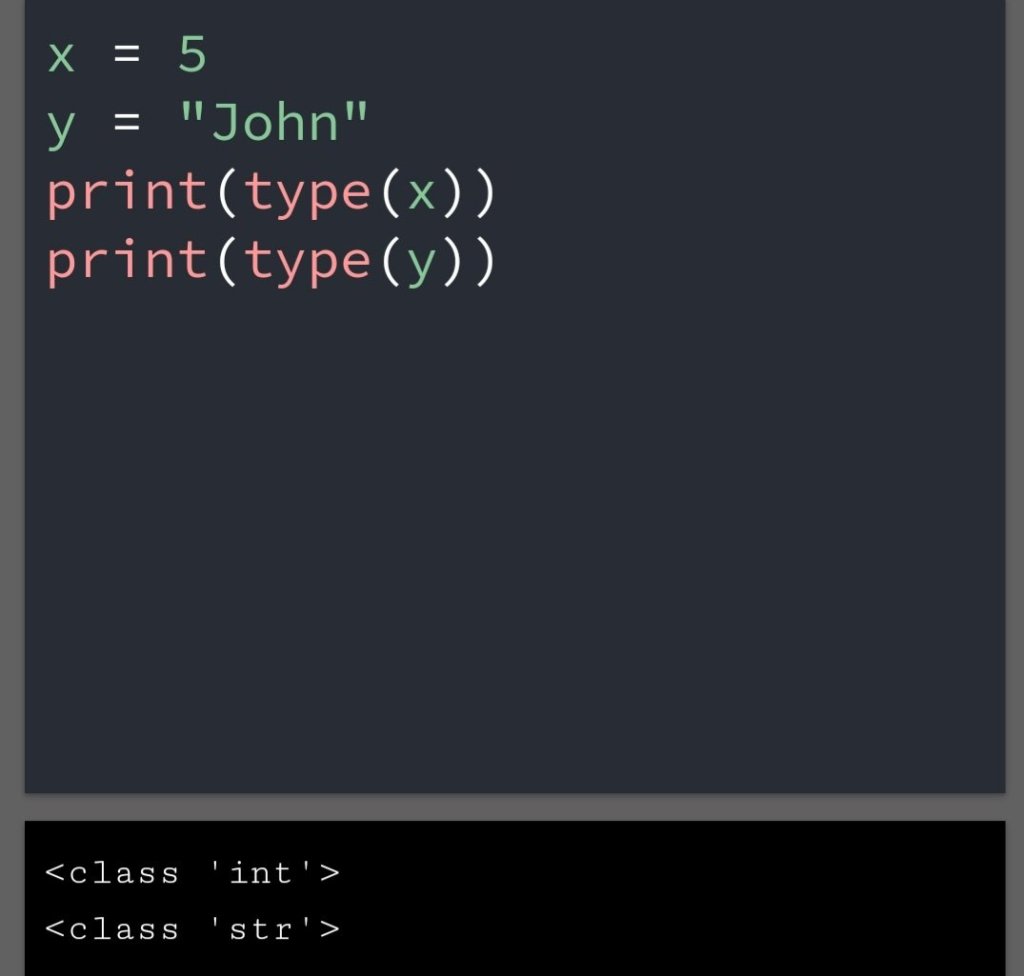
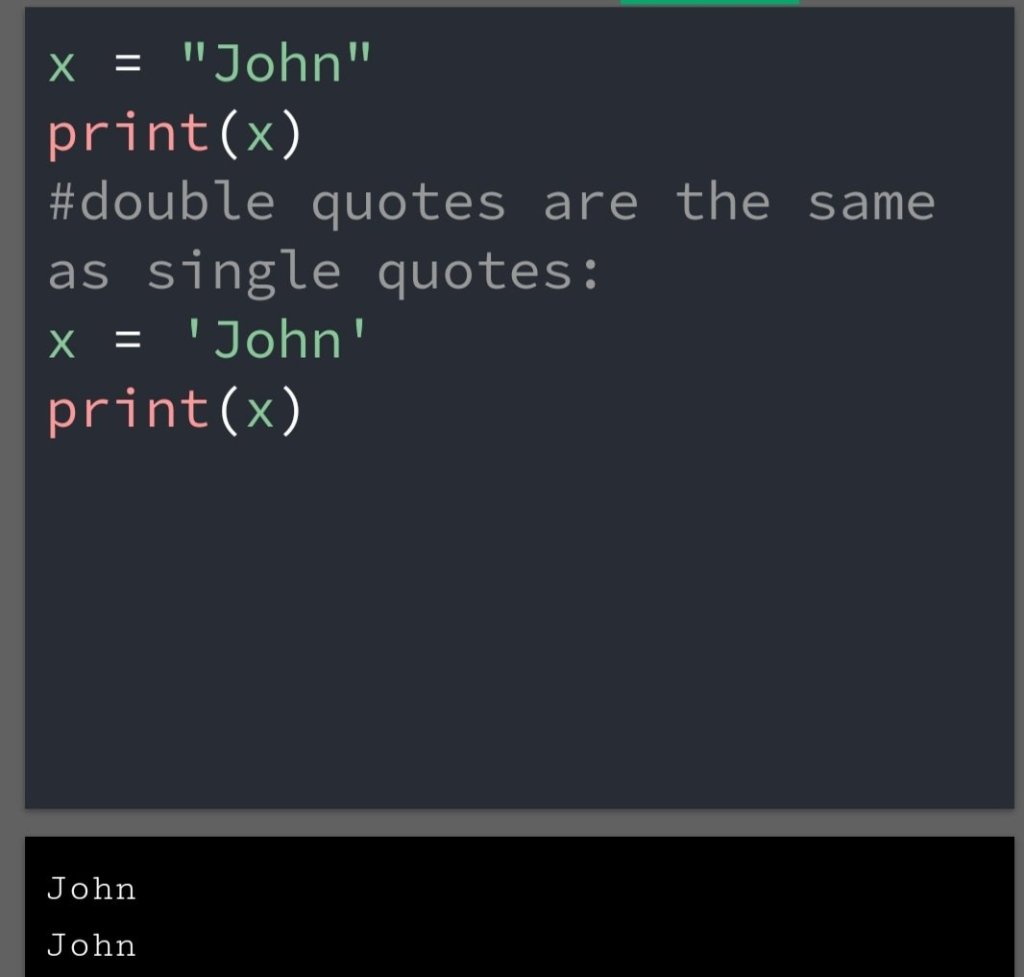
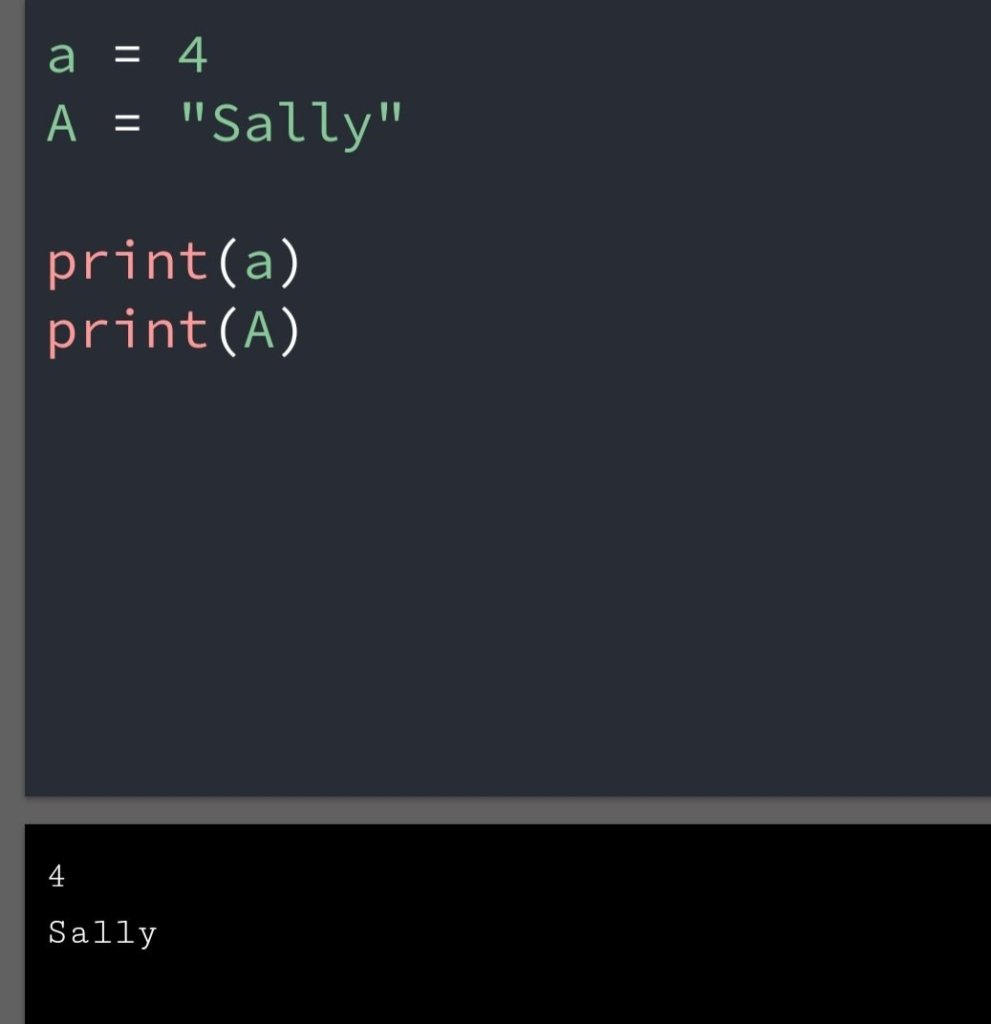
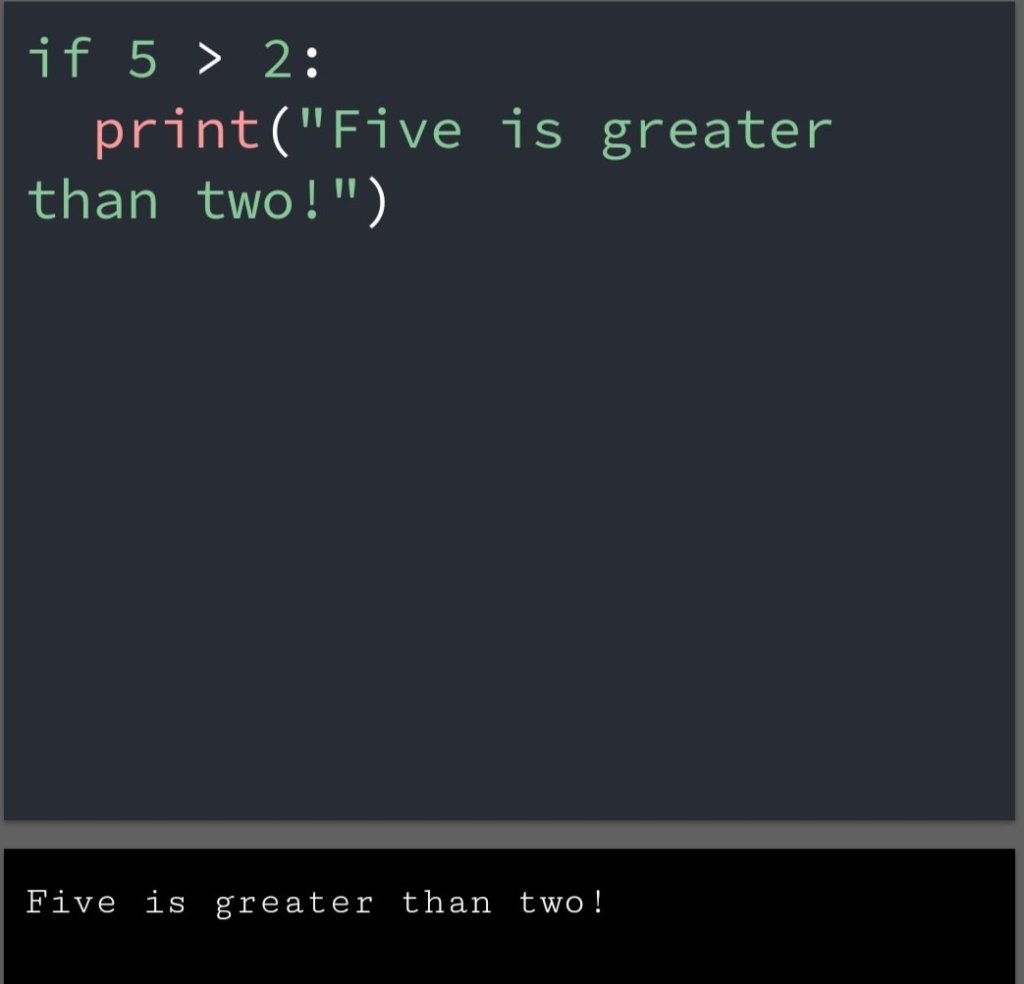
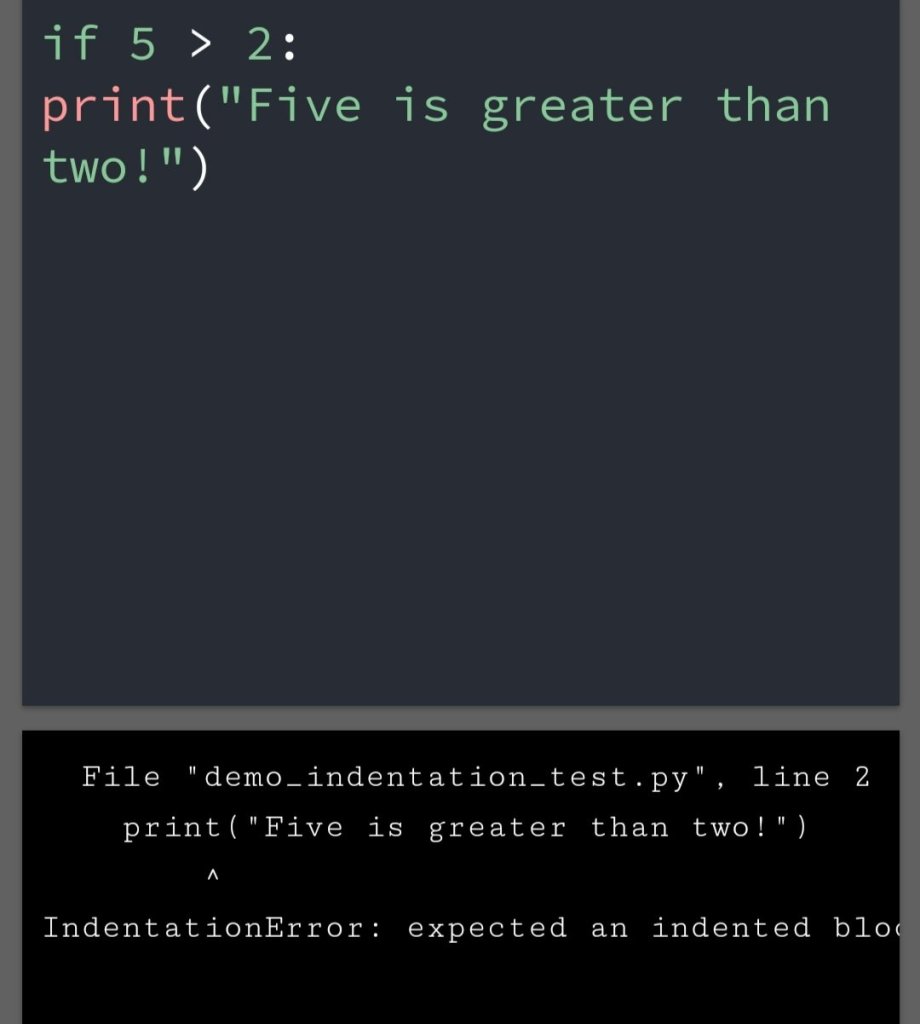
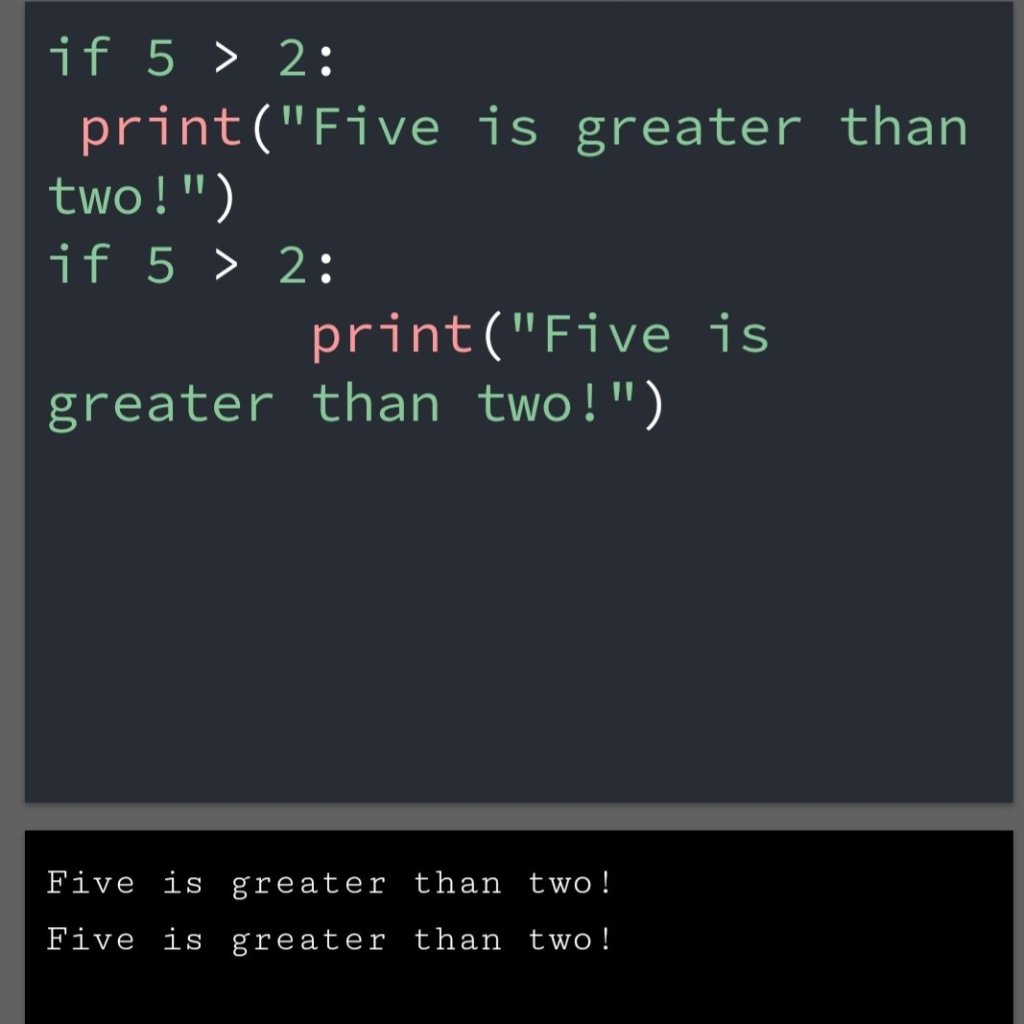
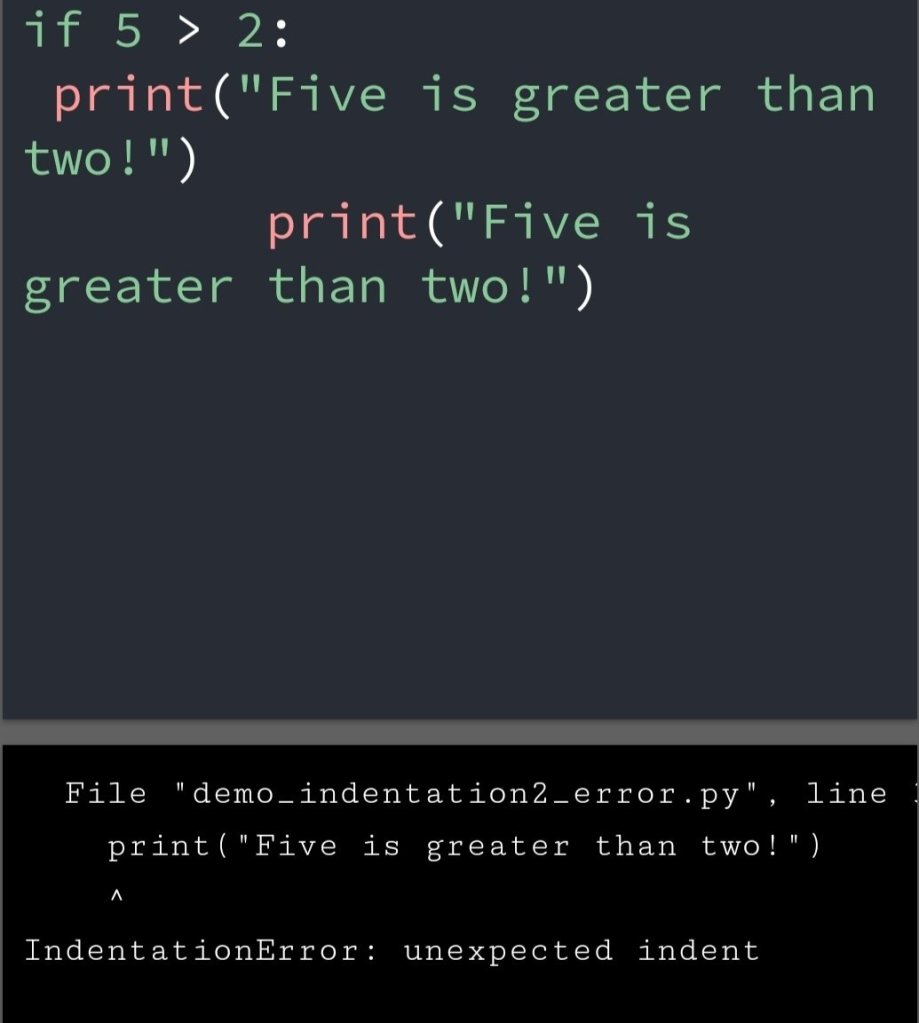
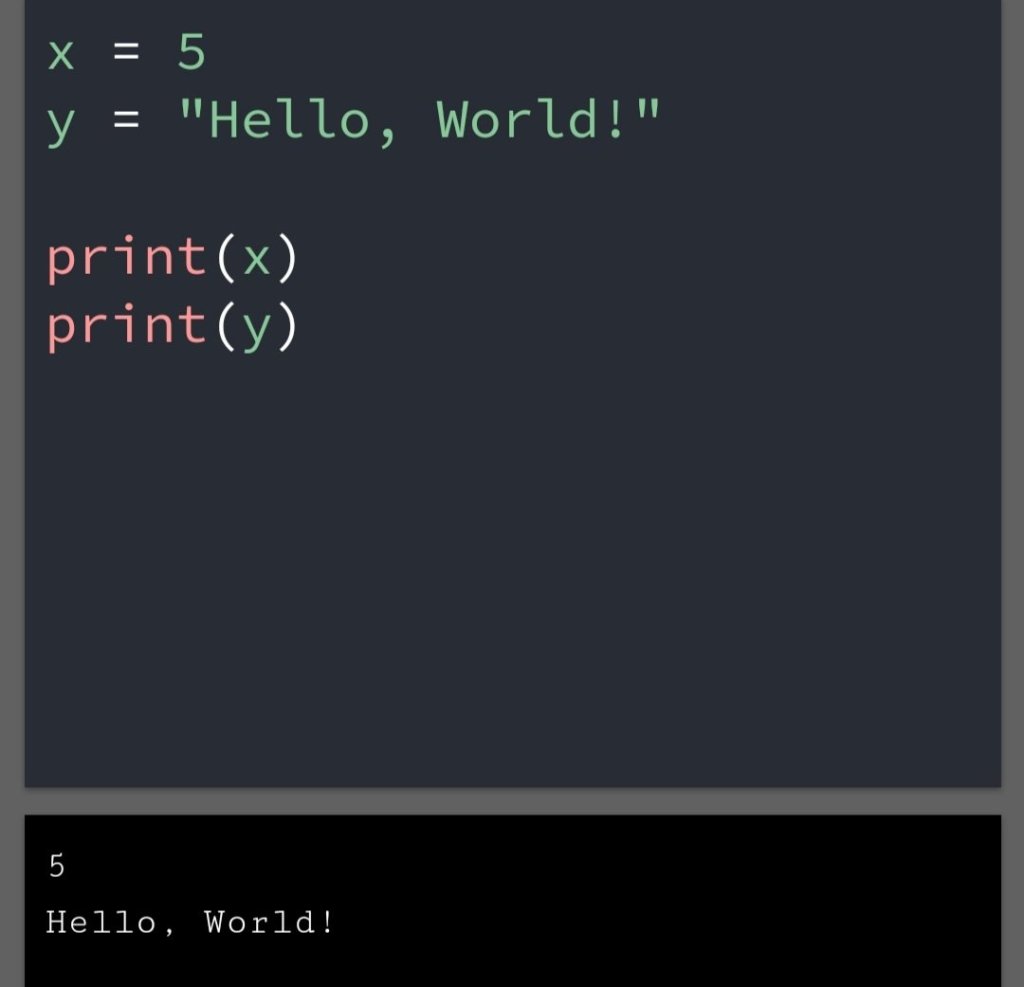
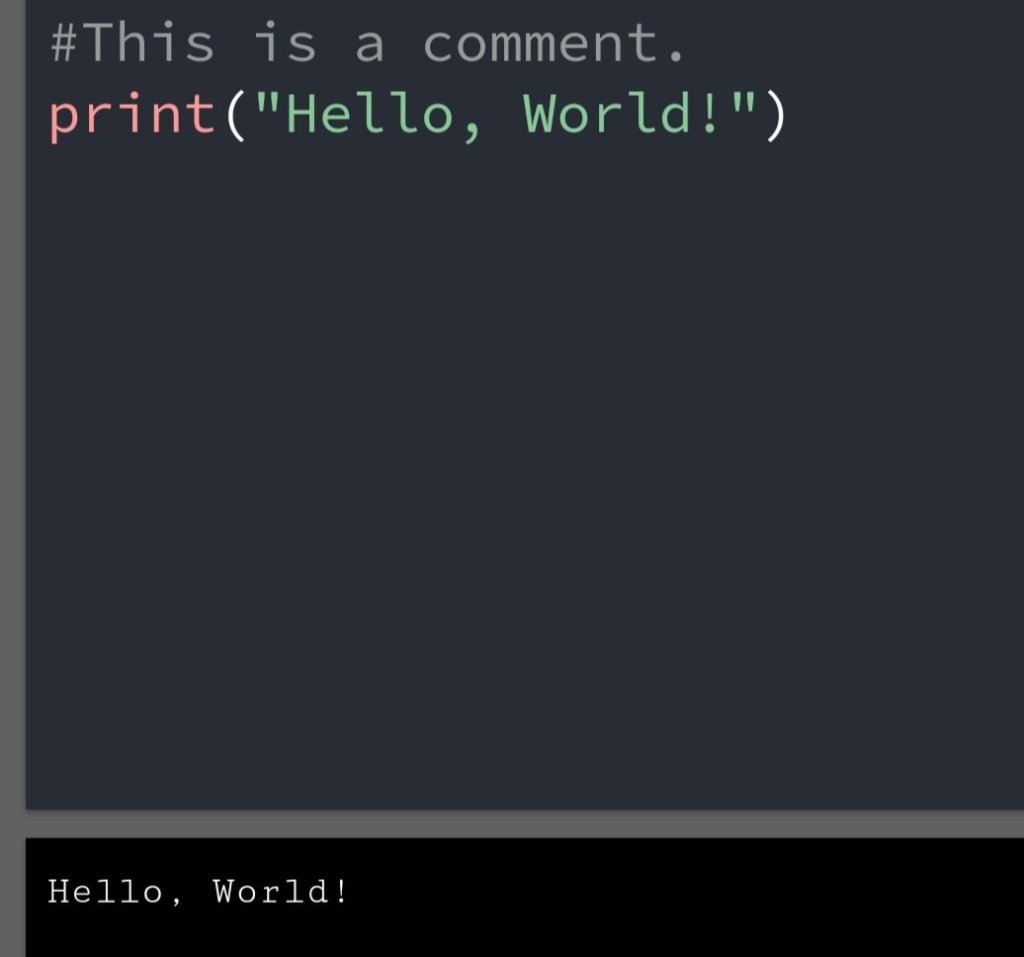
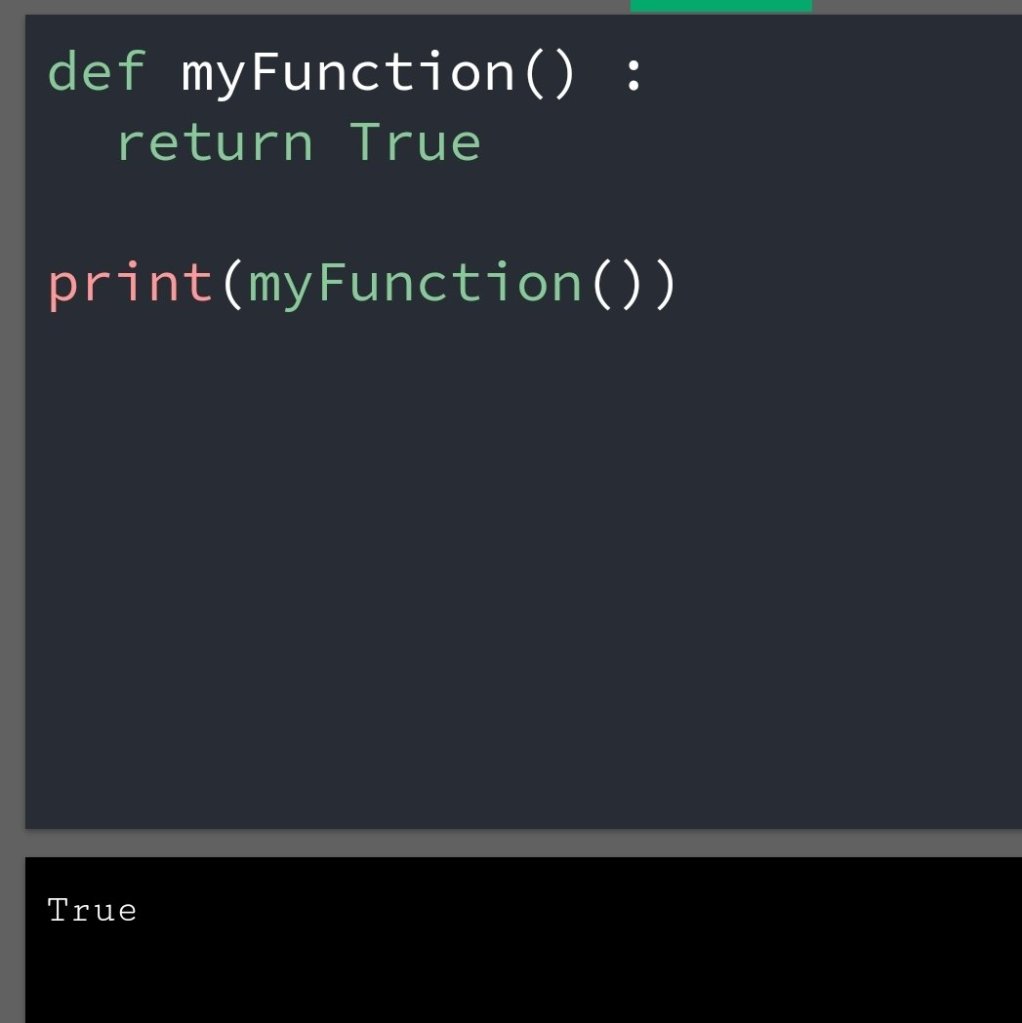
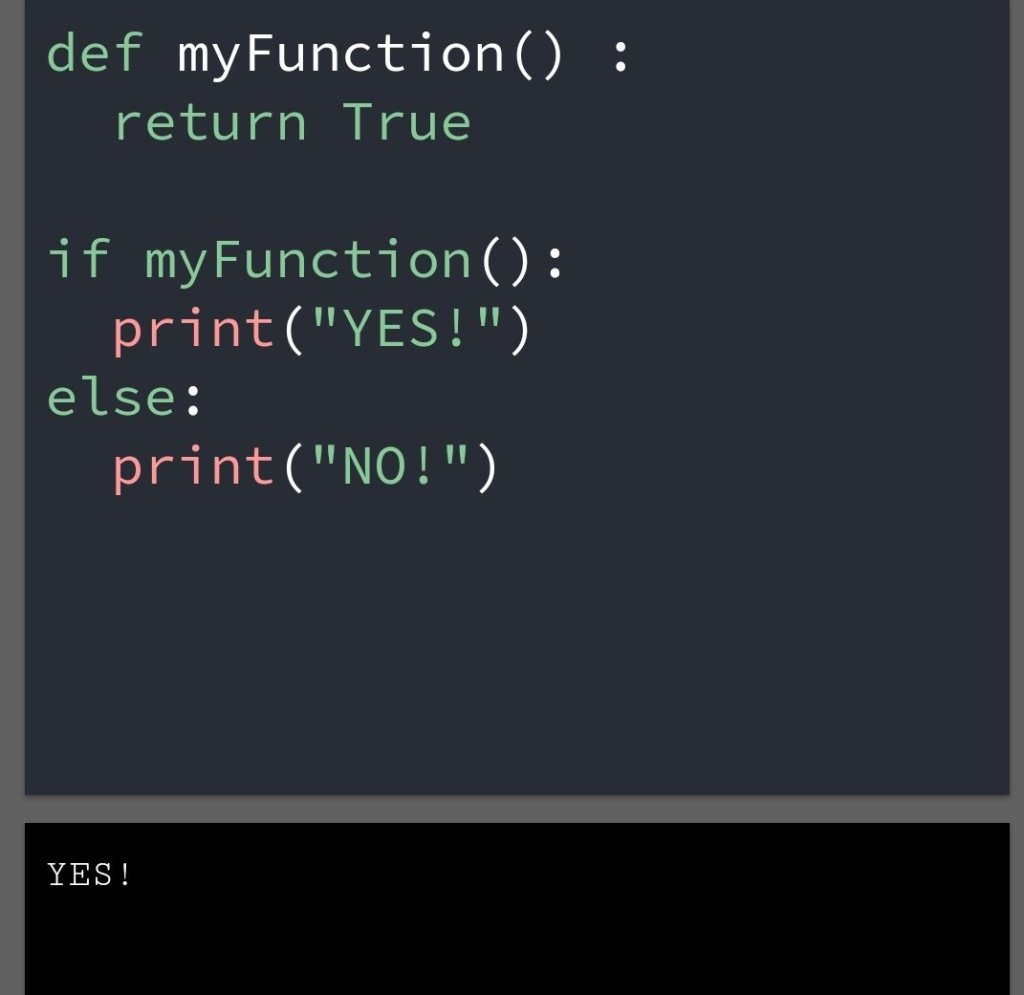
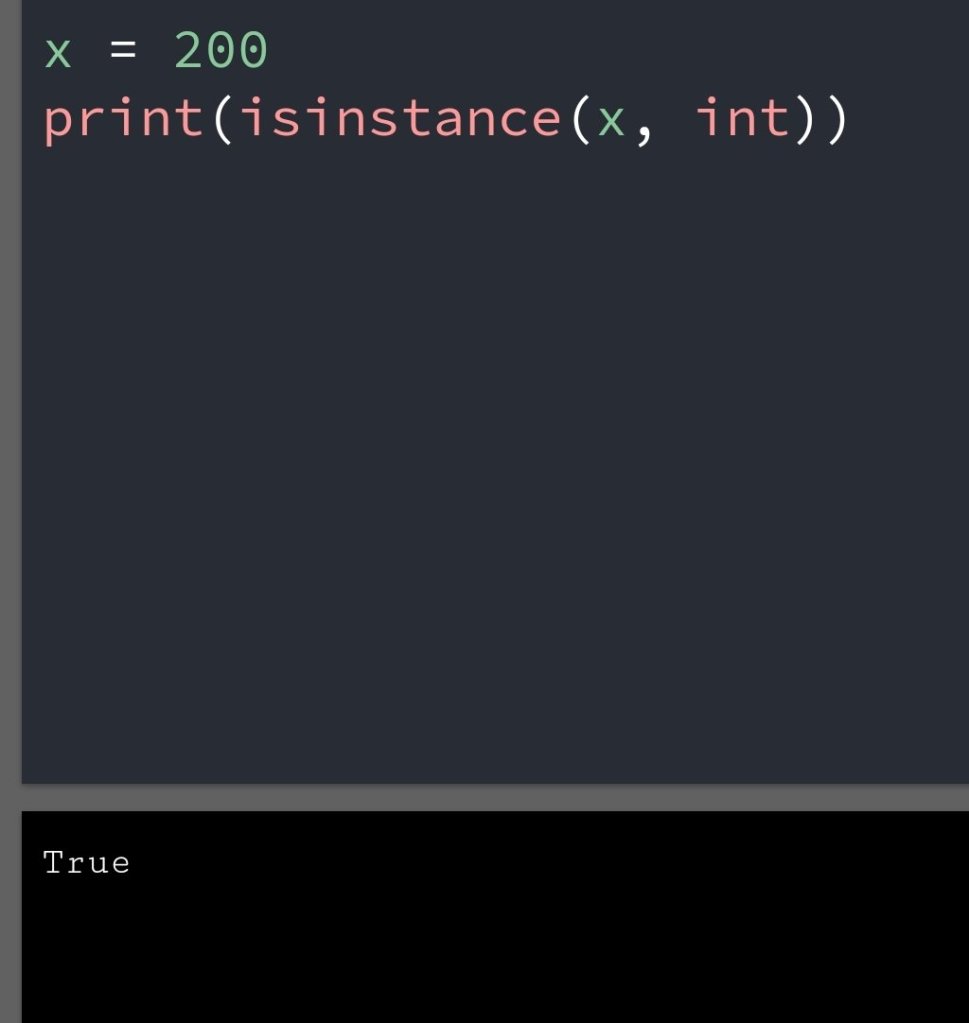
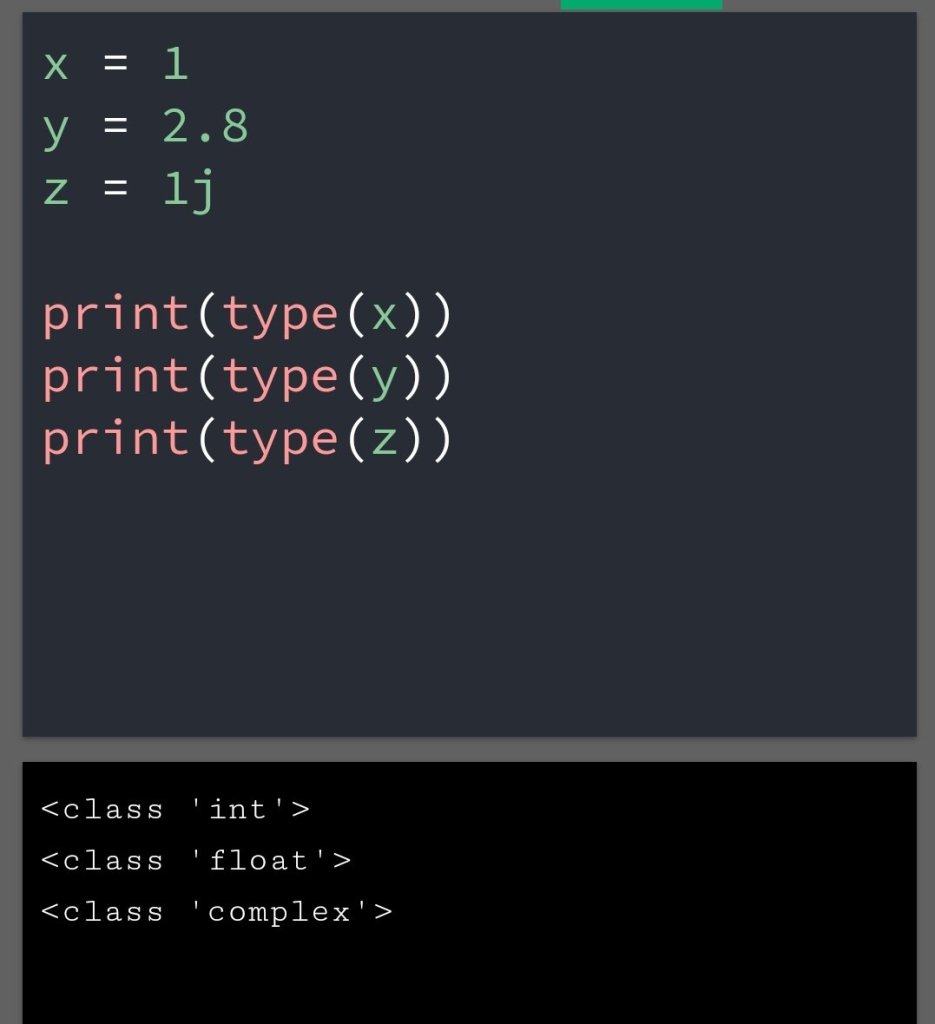
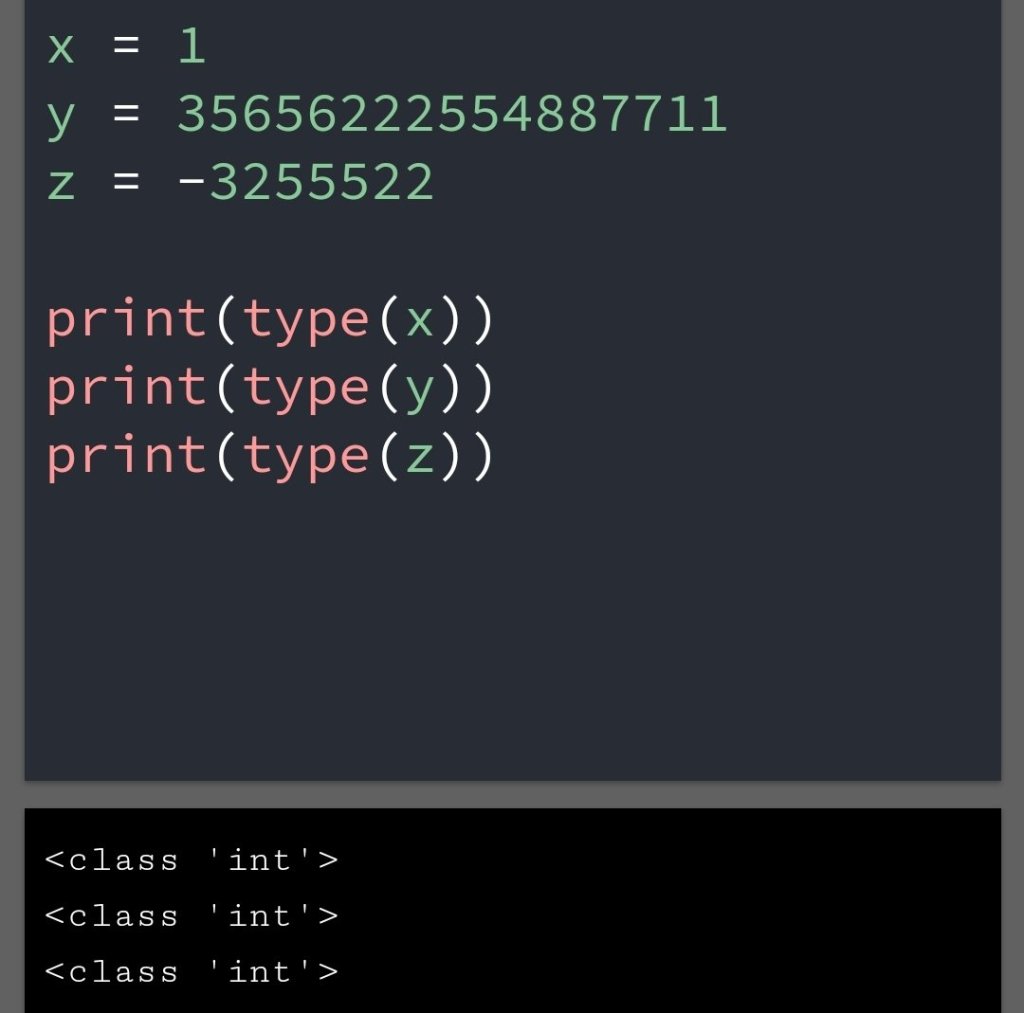
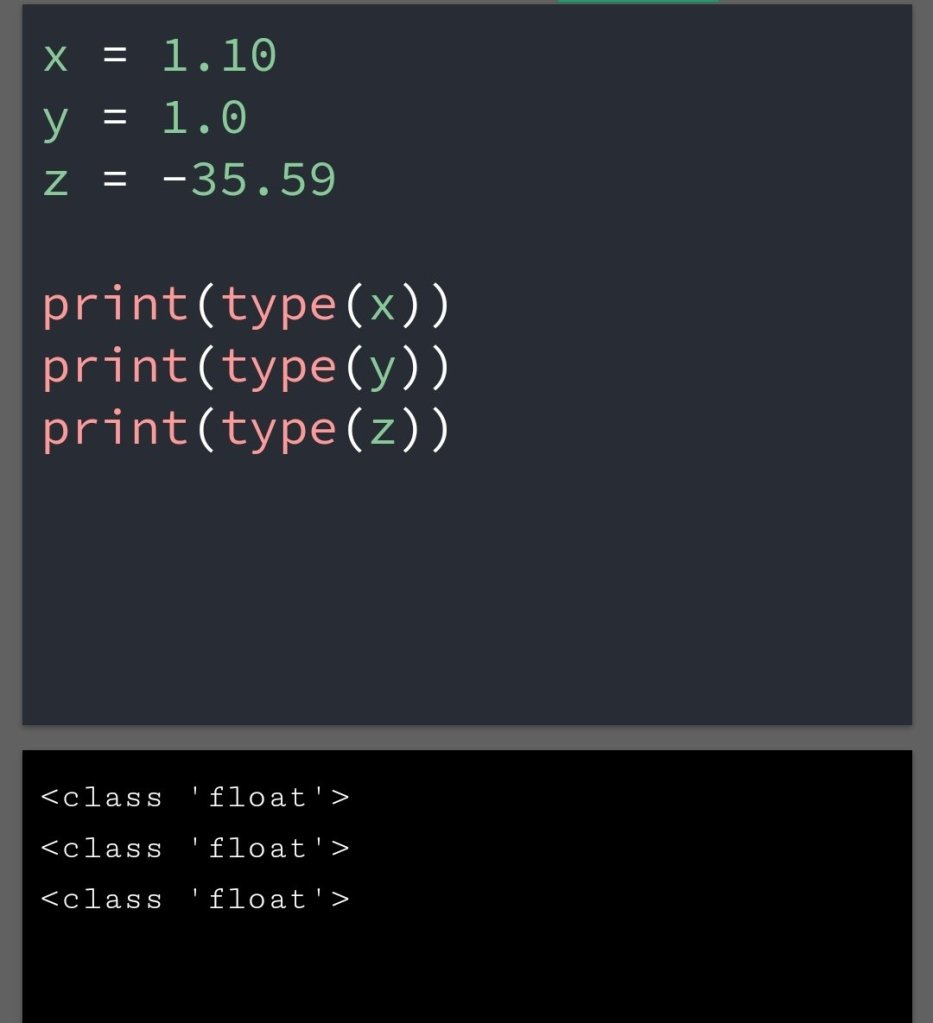
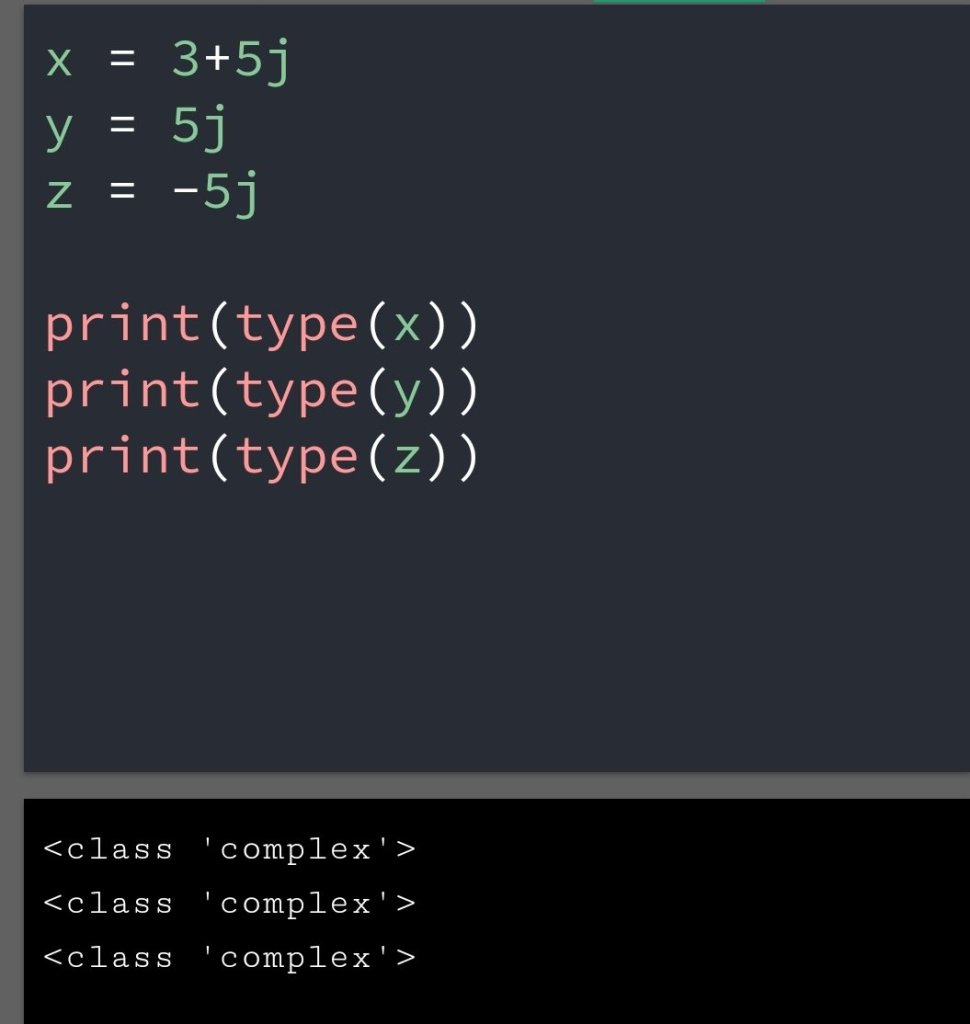
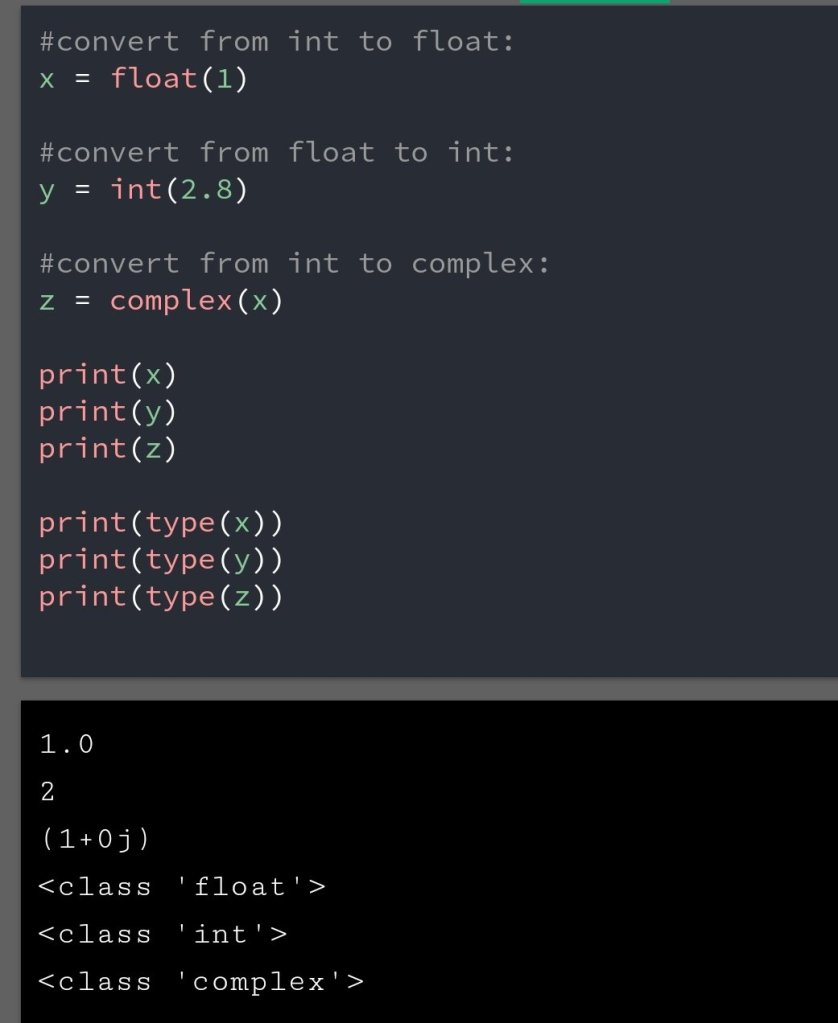
In the previous blog, you had seen some Python List Operations.
Python enthusiastic generally avoid it. Think it is not so important. I am asking you why it’s not important?
Why It’s not so valuable to make a clone of the list, join the two list?
It’s a combination and transformation of one list to another list.
I am creating this blog post to show you how to join the list? How to find the elements in the list?
In this blog, you are going to see:-
• Python – Copy Lists
• Python – Join Lists
• Python – Count method
• Python – List Index method
∆ Python – Copy Lists

You can copy the list with following method:-
• using copy() method
• second is list() method
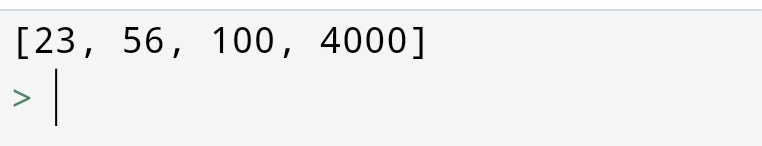
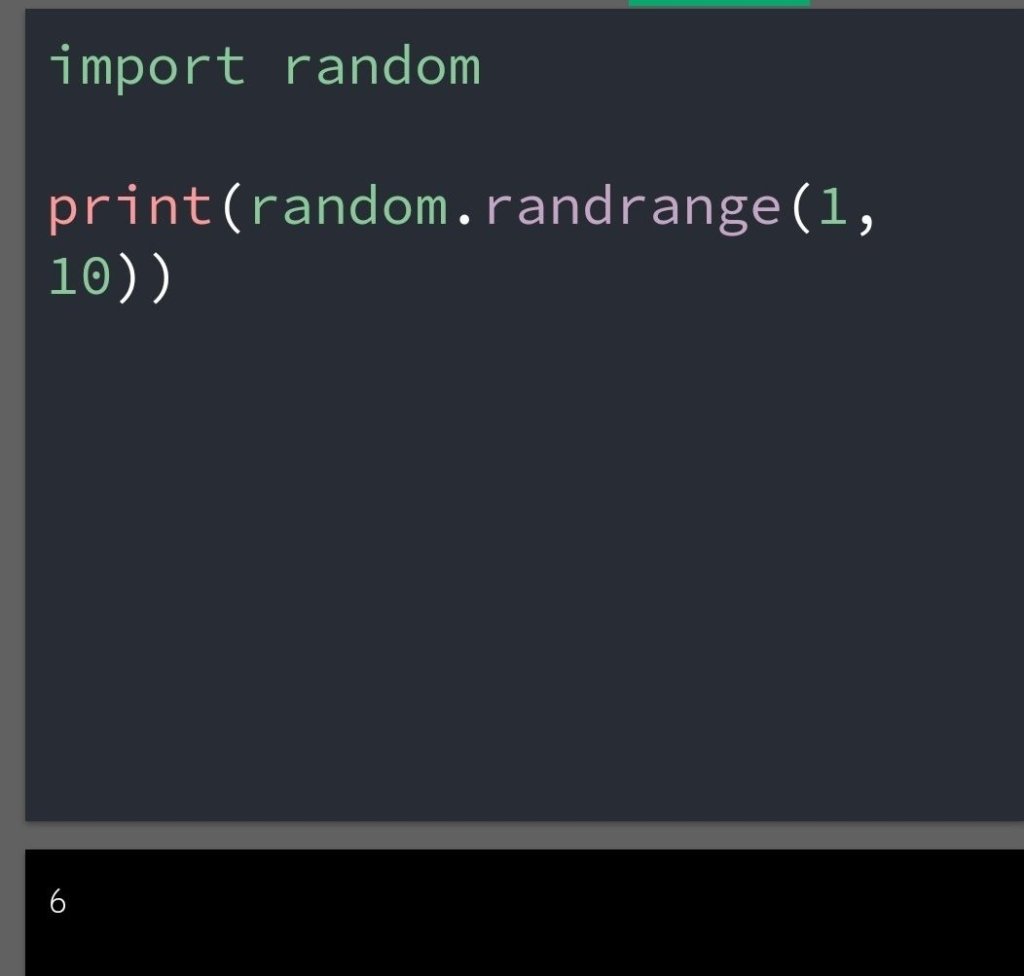
1.Copy Method

Copy method copies the first list into the second list. You can do it with code:
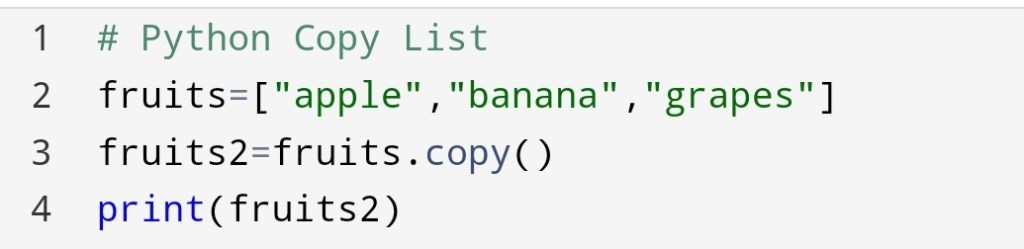

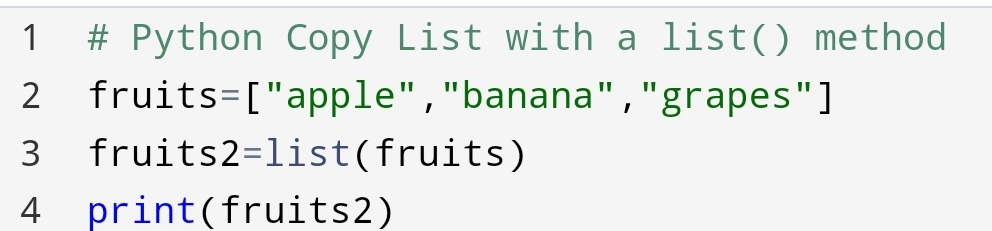
2. Python Copy List: list() method

The second way is to use a list() method to copy a list.
In this method, you will pass the first list to the list() method which will store in the second list.
Let’s see how can you do!

Here, you will observe that the output of copy() and list() method to copy the list is the same. Only the method is different.
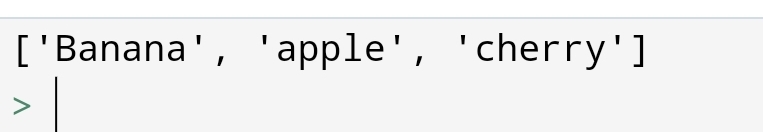
∆ Python: Join the list

Suppose, you have to join the two list. For example, you have to join the list of boys and girls to create one class of students.
Let’s see how can you do it!
You can do it with the following methods:-
• Using + operator
• Append method
• extend method
1.Using + operator
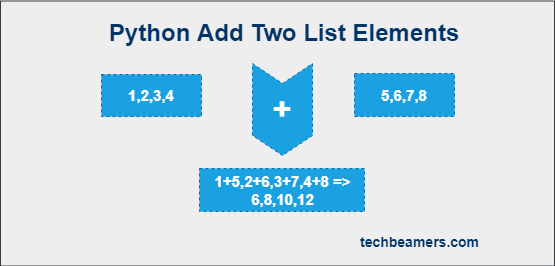
You can join the lists with + operator. + operator joins the second list to the first list.
You can do it with following code:-


2.Append method

You can join the second list to the end of the first list using the append method.
This method appends list2 into list1. Let’s see how can you do!


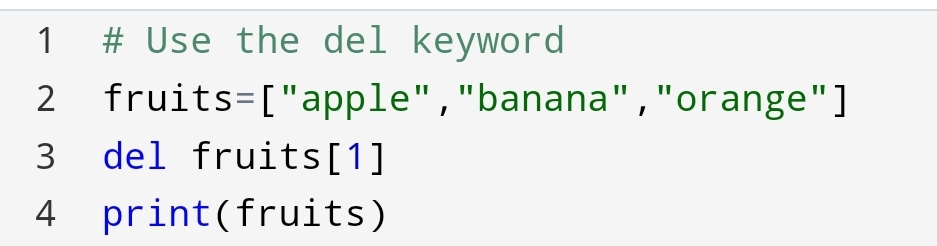
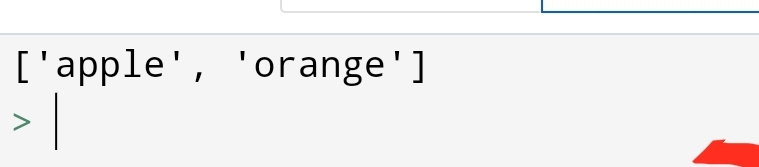
3.Extend method

Suppose you have to join the second list at the end of the first list. So, you can do it with extend method.
You can code:-


∆ Python List: Count method

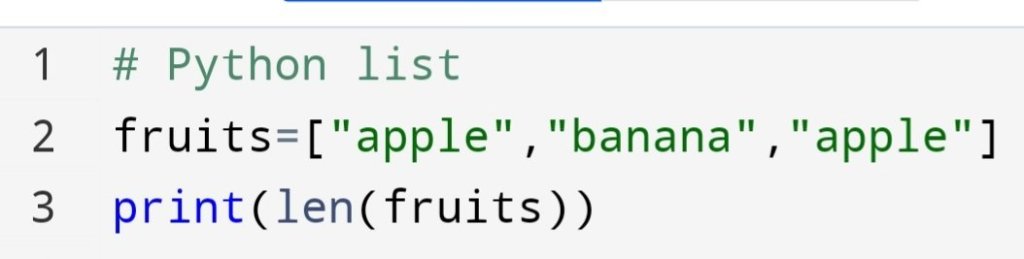
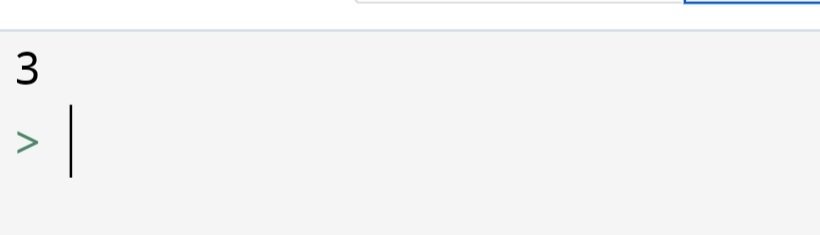
Suppose there is a large group of numbers. In that numbers, you have to find the number of times a certain number has repeated.
So, how will you count?
Well, you will say I am going to count the repeated numbers. It’s good to count. But If there are thousands of numbers it will take 10 to 15 minutes.
But if I say you can do it in 2 minutes. not only thousands but millions of number.
You say it’s amazing! Let’s see how can you do!
You can do it with the count() method. The syntax is count(value).
Value could be str, int, boolean and any type.

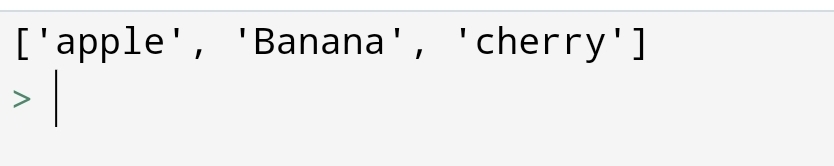
∆ Python List: Index method

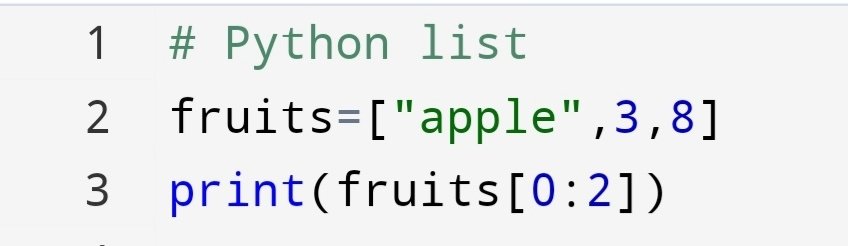
Suppose, you have to know the position of a specific value. so, how can you do it?
Think about it! If the list is short then you can find a position easily.
But if the list has thousands or millions of items. how can you do it?
You can do it with a list index() method.
Let’s see how can you do!
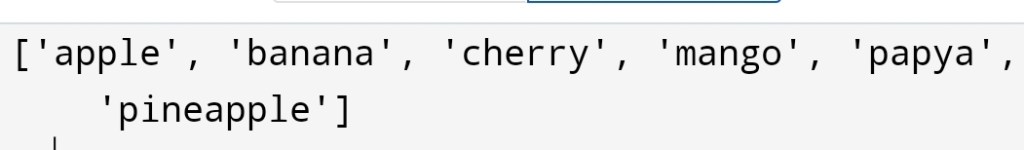
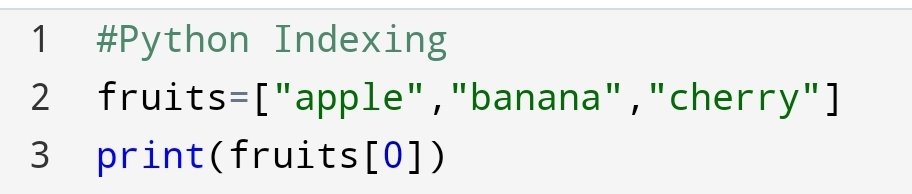
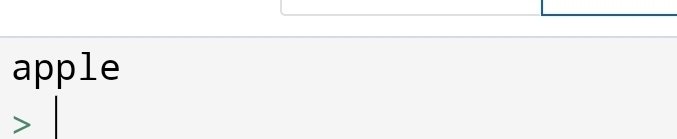
Let’s find the position of “apple” in the list of fruits.


Here, you have seen how can we find a position of a certain value. It’s no so much hard! We have to find why are we doing it? It’s amazing.
Python list gives freedom to create a new list easily. It’s going to give insight into how can you store and manipulate data.
Conclusion:-
In this Python list blog, you had seen how to transform two lists into one list using join and copy method.
You can also find the position and count the value in the list using the index() and count() method.
I hope you liked this blog. This is the third part of the python list. I have tried everything in this blog.
If anything remains, please comment to me. I will create a blog on that topic.
Also, If you will find some mistake you can comment on me at vipulkunwar341.
For additional information, you can visit Python list w3schools.
See also:-
For more contact detail you can mail at: