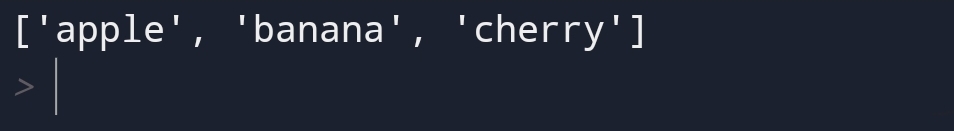
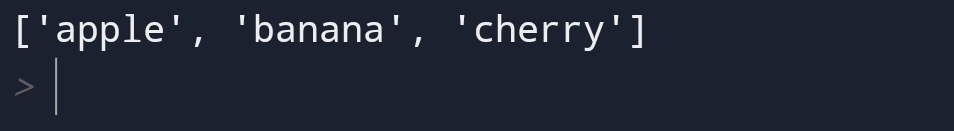
Doing the same task is boring. Also, the same thing in python is boring. So what’s the solution?
The conventional solution could be to do the program again and again but it becomes frustrating.
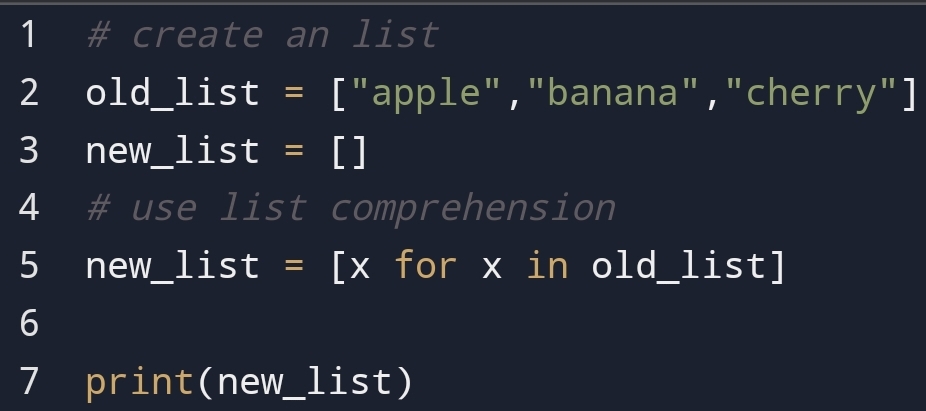
So, you can use the python function. You will tell me what’s the python function?
How can I automate the repeated task?
I’m going to show you what’s the python function? How can you use it? And what’s the benefit of using it?
What’s the python function?
The python function is a process where you can do repeated tasks easily. For example, passing numbers through function.
Whenever you want to repeat a task you can just call the function.
So, your next question how it looks like?
The appearance of the python function shows
def function_name(args):
In the above syntax you can see that I have started the function with def keyword.
The meaning of the def keyword is to define the function name.
After the def keyword, you can see that I have passed the arguments with parenthesis and at last semicolon(:).
Remember, it’s the starting point of function, not the whole structure of the function.
When you move forward in the blog you understand the structure of the python function.
Use of docstring
You will be amazed,” I have known about string”. But What’s the docstring?
Don’t be amazed it’s the element of the python function which explains what are you doing in function?
It looks like:-
def function_name(args):
""" what the
function doing"""
You can say, docstring in function is similar to comment in python.
Remember, docstring use triple quotes for comment.
Till this point I have define function name, argument and docstring.
The next point I’m going to show you is the statement or output which going to display on the computer screen.
Return statement in function
The return statement returns the statement after calling the function.
It ends the execution If the function calls and returns the result.
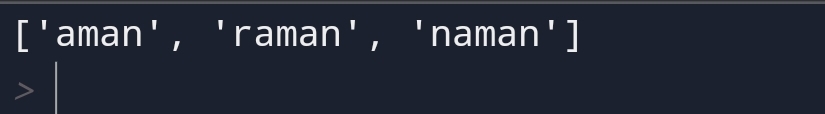
For example,

Output:
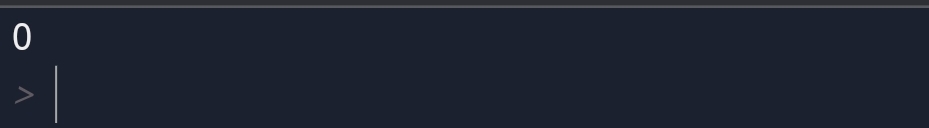
If the return statement is without any expression then the special value none is returned.
For example,

Output:
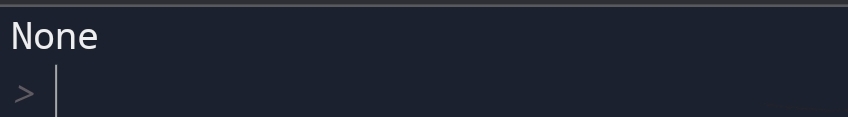
You can see that If there is no expression in the return statement result will be None.
So, you would say why the None value?
None value means no expression in the return statement.
Passing the value
You can pass the value from a function to display the output with the passed value.
For example,
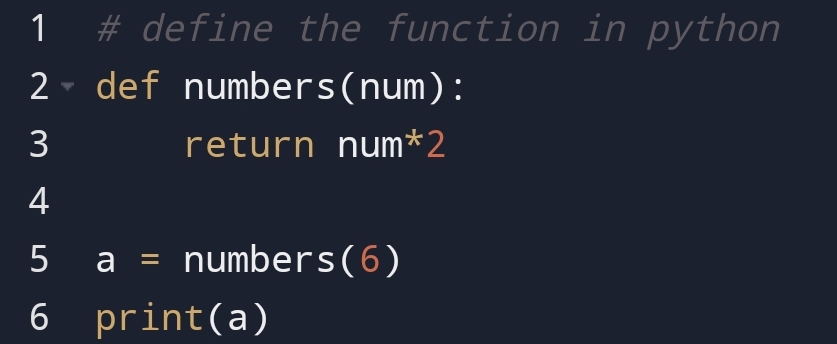
Output:

In here, you can see that I have passed the number 6 and the result has come.
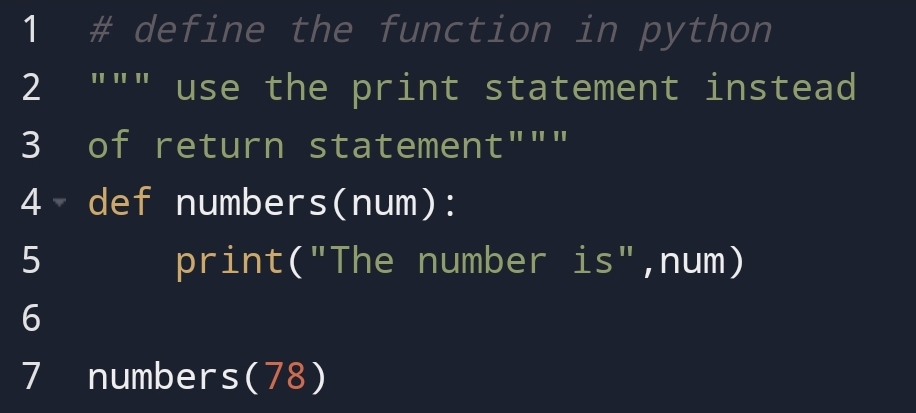
You can also pass the value without a return statement. But output will display with a statement.
For example,
Output:

In the above example, you can see that output has come with a statement.
Arbitrary and keyword argument
In the next part of the blog, you are going to see what’s the arbitrary and keyword argument.
So, let’s see how can you passed the value in different way.
When number of arguments are not fixed!
Suppose, In a function, you don’t know how many values or arguments are going to pass. You can use arbitrary keyword.
You will be amazed what’s the arbitrary keyword?
You are going to see what’s it?
The arbitrary keyword is an asterisk(*) sign with arguments that permit you to pass as many arguments as you want to pass.
You can relate to this example.
For example,

Output:
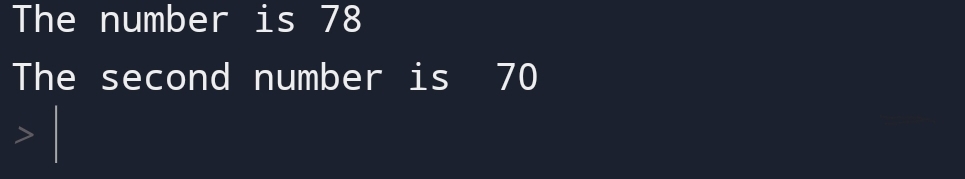
In the above example, you can see that I have displayed the two numbers in a different statement.
Remember, the arbitrary argument is accessed using indexing.
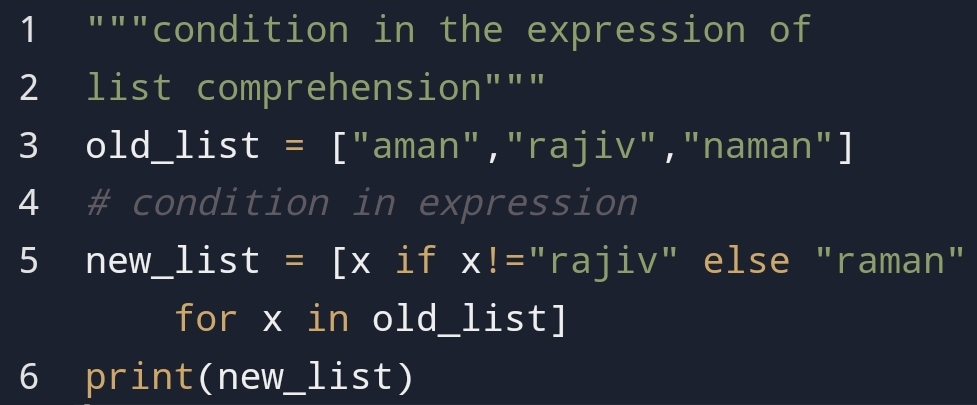
Pass the argument as key-value pair!- Keyword argument
You can use a keyword argument to pass the key-value pair from the function.
For example,
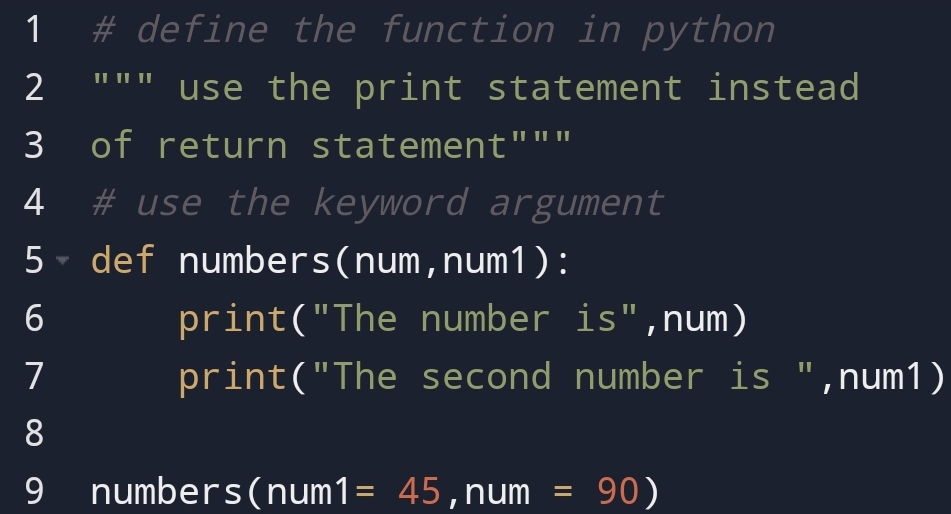
Output:

So, you would say what’s the benefit of keyword argument.
If you clearly see that I have given first position to num1 even in function num position is first.
What’s that mean?
That means you don’t care about the order of the argument. You can put in any order with the help of the keyword argument.
In the above example, you had seen how can you pass arguments in any order.
You don’t know how many keyword arguments- **Arbitrary keyword argument
You can see what I’m going to do in this section with the heading.
I’m going to show you what’s the benefit of an arbitrary keyword argument!
You can pass as many as keyword argument using **Arbitrary keyword argument.
You can use a double-asterisk(**) sign to indicate this.
For example,

Output:

In the above example, you can see that I have passed multiple keyword arguments using ** double-asterisk.
How can you display value of the key?
You can display the value of the key using the key in the print statement.
Pass statement in python- make an empty function!
You can use the pass statement in the python function if you don’t want to execute the function.
Perhaps, you would say, ” We will not give print or return statements”.
You thought right but It will give an error.
For example,

Output
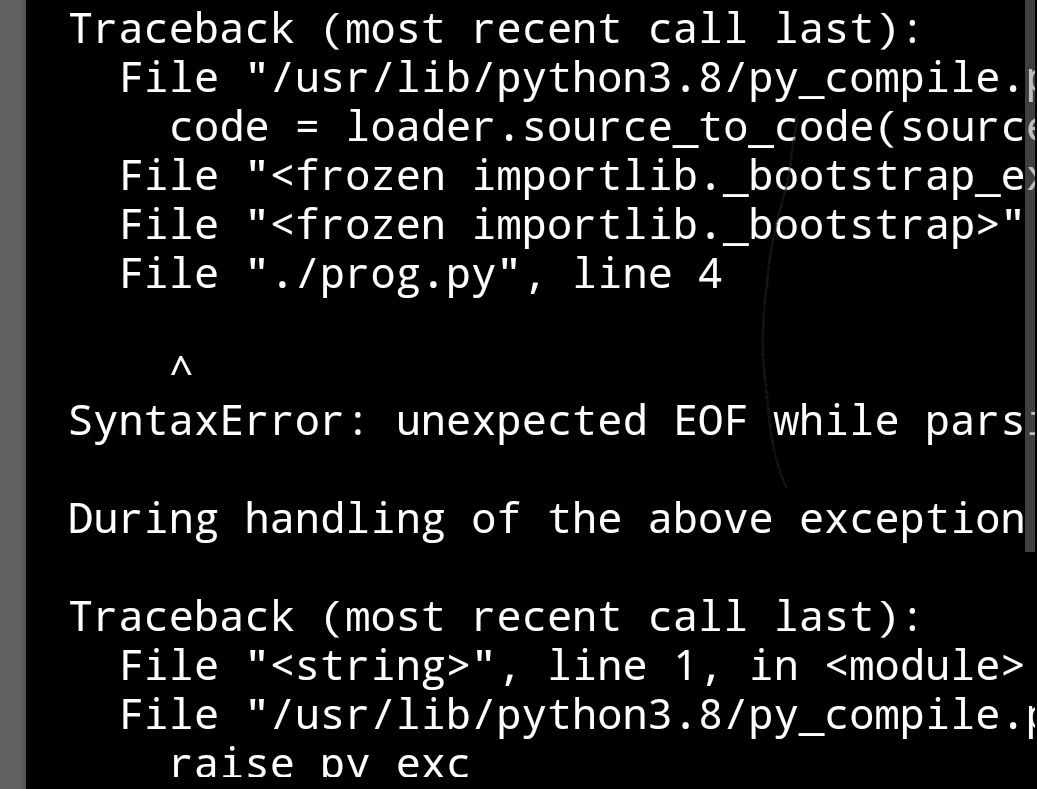
In the above example without a pass statement, it has given a syntax error.
You can use a pass statement in to prevent errors.
For example,

Output

In the above example, you can see that when I have used the pass statement no error has came.
Conclusion
You can repeat the task in python using function.
Function taking arguments to return value. These values are returns using the return statement.
You can use arbitrary arguments to return as many as the value you want.
Using keyword argument you don’t need to care about the order of function argument.
So, what do you think about the python function? Is there anything I have not covered? And you want to cover, comment on it!
I hope you feel it!
For more: visit
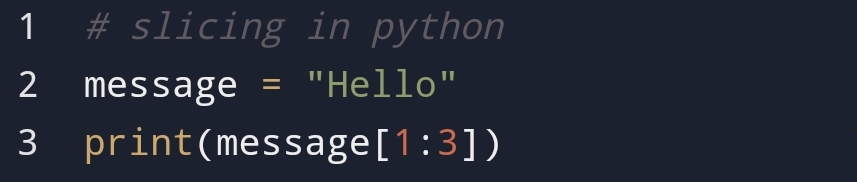
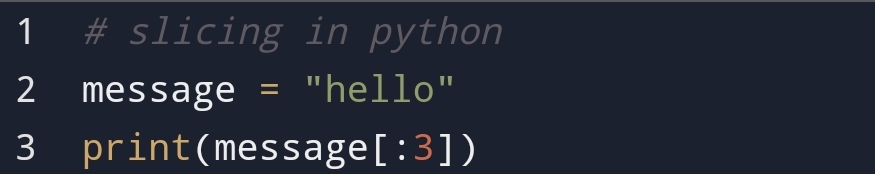
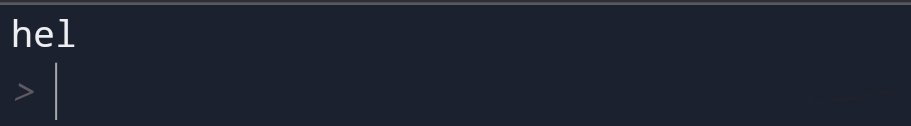
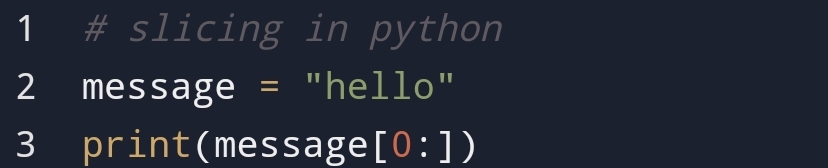
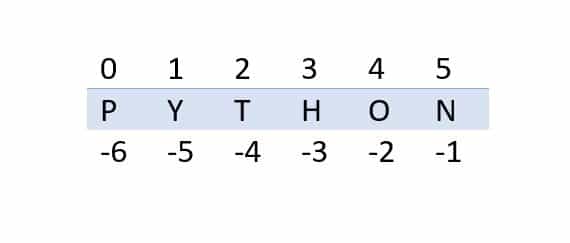
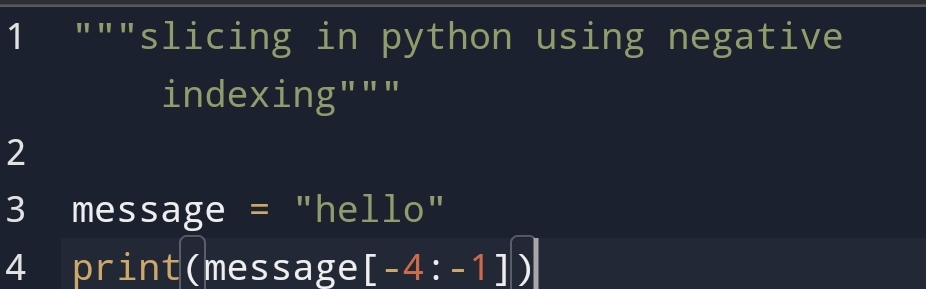
• Why python slicing is
important?
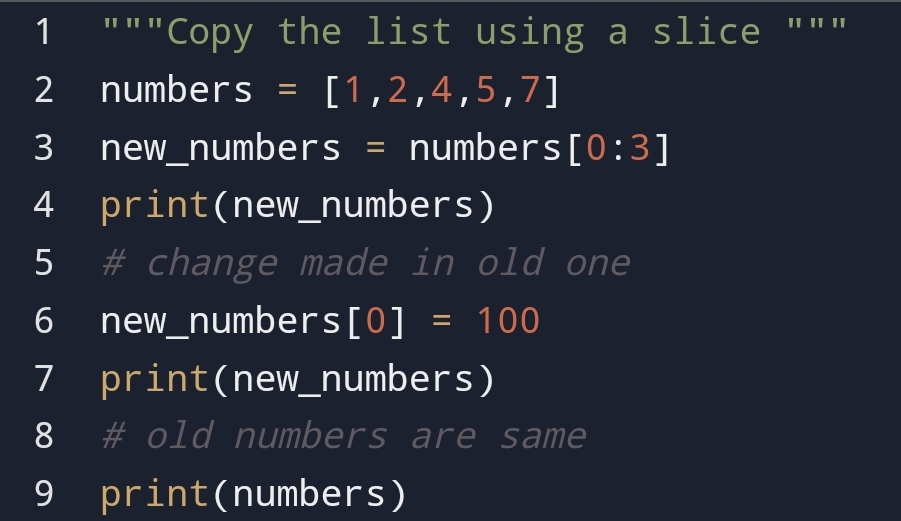
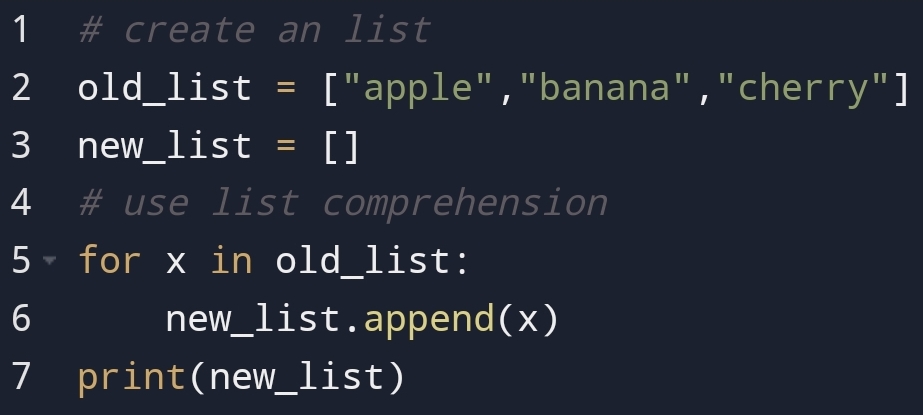
• Create a list with
short syntax!
• Core values of python!
"Quality brings clarity "